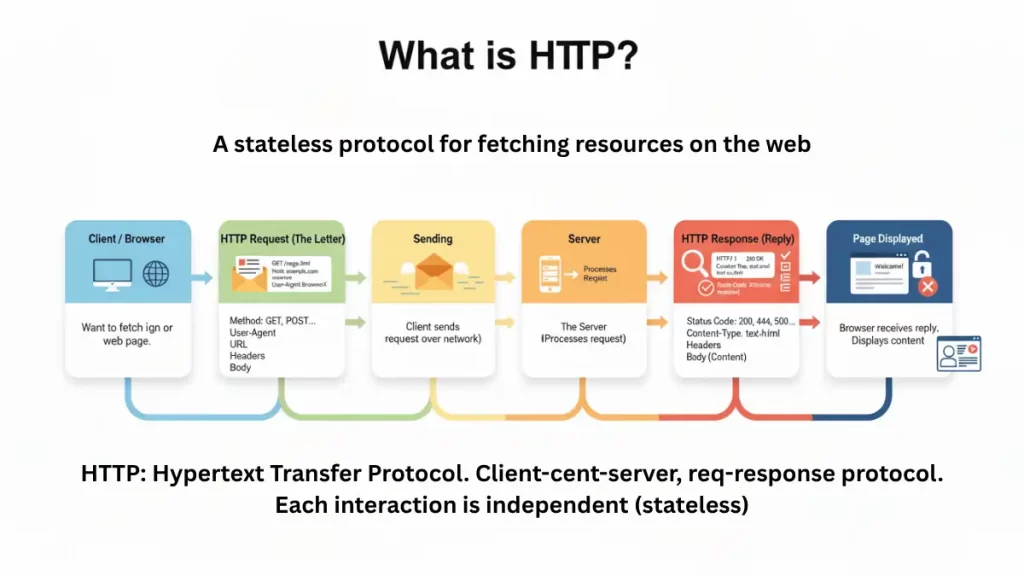
Definition: Hypertext Transfer Protocol is the application layer protocol most web APIs use to exchange requests and responses. It defines methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, status codes, headers, and message bodies. Modern APIs typically run over HTTPS, which wraps HTTP in Transport Layer Security to encrypt traffic and verify server identity. HTTP/2 introduces multiplexed streams over one connection, improving latency, while HTTP/3 builds on QUIC. Intermediaries such as proxies, gateways, and CDNs can observe or modify headers and caching behavior. Understanding method semantics and idempotency helps design predictable APIs and safe retries. Content negotiation selects formats via headers wisely.
Example: A server returns 200 OK with a JSON body.
Also called: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
Related: Header, Status code, REST (Representational State Transfer)

