Definition: A family of chemically strengthened glass used on phone screens and backs. It resists scratches and shattering better than regular glass by swapping ions during a salt bath process, which compresses the surface. Exact version and durability vary by model. Using a case and avoiding drops still helps most.
Corning Gorilla Glass is a brand of chemically strengthened glass developed and manufactured by Corning Inc. It’s designed to be thin, light, and durable, making it ideal for the screens of mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops, as well as wearables and other electronic displays.
Here’s a breakdown to help you understand it better:
What makes it special? The Ion-Exchange Process
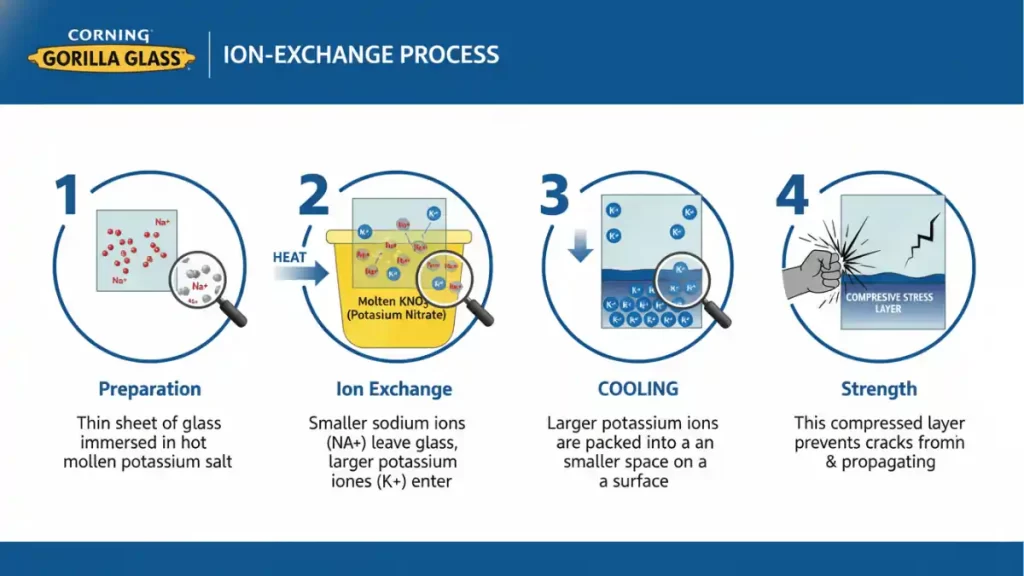
The key to Gorilla Glass’s strength lies in a process called ion-exchange. Here’s how it generally works:
- Preparation: A thin sheet of glass is immersed in a hot bath of molten potassium salt.
- Ion Exchange: At high temperatures, the smaller sodium ions in the glass migrate out of the material and are replaced by larger potassium ions from the salt bath.
- Compression: When the glass cools, these larger potassium ions are “stuck” in a smaller space, creating a layer of compressive stress on the surface of the glass. Think of it like a tightly stretched spring.
- Strength: This compressed layer makes the glass much more resistant to damage from impacts and scratches. It’s harder for cracks to initiate and propagate through this compressed surface.
Key Characteristics and Benefits:
- Damage Resistance: Its primary benefit is its high resistance to scratches and impacts, which are common causes of screen damage in portable electronics.
- Thinness and Lightness: It can be manufactured very thin without compromising significant strength, allowing for sleek device designs.
- Optical Clarity: Gorilla Glass maintains excellent optical clarity, crucial for vibrant displays.
- Touch Sensitivity: It doesn’t interfere with the touch sensitivity of screens.
- Environmental Friendliness: Corning states that its manufacturing processes are environmentally conscious.
Evolution and Versions:
Corning has continuously improved Gorilla Glass over the years, releasing various generations, each offering enhanced durability, scratch resistance, or other features.
- Gorilla Glass 1: Introduced in 2007, famously used in the original iPhone.
- Gorilla Glass 2: Thinner and lighter than GG1 while maintaining similar strength.
- Gorilla Glass 3: Introduced “Native Damage Resistance” (NDR) technology, making it more resistant to deeper scratches that often lead to glass breakage.
- Gorilla Glass 4: Focused on improving drop performance, making it more likely to survive drops onto rough surfaces.
- Gorilla Glass 5: Even better drop performance, designed to survive drops from up to 1.6 meters onto hard, rough surfaces.
- Gorilla Glass 6: Further improved scratch resistance and drop performance, designed to survive multiple drops from 1 meter.
- Gorilla Glass Victus / Victus 2: These versions represent a significant leap, combining excellent drop performance with significantly improved scratch resistance, aiming to be a “best of both worlds” solution.
Where you find it:
You’ll find Gorilla Glass on a vast majority of premium smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and even some laptops and automotive displays. Many manufacturers highlight its inclusion as a key feature for device durability.
Example: A screen survives keys in a pocket thanks to Gorilla Glass.
Also called: Gorilla Glass
Related: IP68 rating

