When 14-year-old Sewell Setzer took his own life in January 2024 after months of intensive, emotionally dependent conversations with a Character.AI chatbot, the AI industry faced a reckoning. His mother’s lawsuit alleged that the platform had no meaningful safeguards for minors, no content restrictions, and no warnings about addiction-like patterns. That tragedy became the catalyst for an overdue conversation: If millions of teenagers use AI chatbots daily, shouldn’t they have meaningful protections?
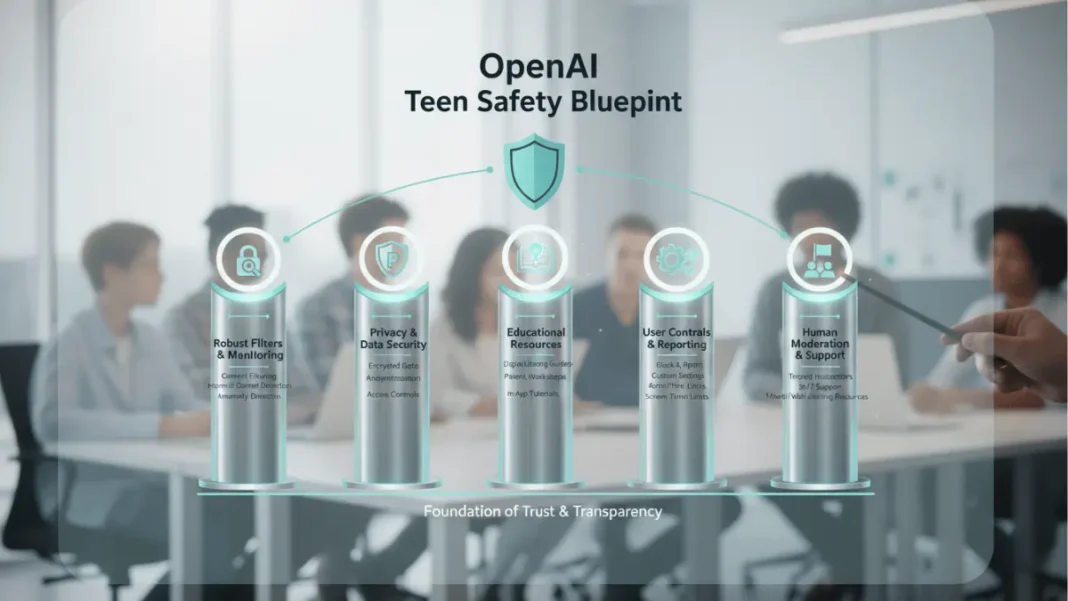
On November 6, 2025, OpenAI answered that question with its Teen Safety Blueprint, a comprehensive framework designed to protect young users while balancing their need for educational access and autonomy. This isn’t a ban on teen usage, it’s a thoughtfully designed set of guardrails featuring age prediction systems, content restrictions, parental controls, and ongoing research collaboration. It’s also, strategically, a proactive move to shape regulation before lawmakers mandate a blanket ban like some are proposing.
In this guide, we’ll explore what the blueprint actually does, how it works in practice, what it can’t yet solve, and what it means for parents, educators, and the future of AI regulation.
Table of Contents
What Is the OpenAI Teen Safety Blueprint?
The Teen Safety Blueprint is OpenAI’s publicly released framework for building AI tools responsible for users under 18. Launched November 6, 2025, it outlines five key pillars: age identification, age-appropriate content policies, parental controls, research-informed design, and transparency. Rather than waiting for regulation to crystallize, OpenAI is implementing the framework across ChatGPT now and positioning it as the industry standard for policymakers writing AI safety legislation.
The blueprint comes after months of legal pressure. Beyond the Character.AI lawsuits, OpenAI faced FTC inquiries and a wave of new state laws. California’s SB 243, signed into law in October 2025 and effective January 2026, requires AI chatbots to include session reminders for minors, parental consent options, and annual safety reports. New York passed a companion AI law in May 2025 banning sexual or romantic chatbots for minors entirely. Congressional hearings in September 2025 proposed even more restrictive federal measures. In that climate, OpenAI’s blueprint reads as: “Here’s how to do this responsibly, trust our approach instead of outright bans”.
Quick Answer: The Teen Safety Blueprint is OpenAI’s framework for protecting ChatGPT users under 18, featuring age prediction, content restrictions, parental controls, and research partnerships. Released November 2025 in response to Character.AI lawsuits and new state AI laws, it aims to set industry standards while allowing minors to use AI safely.
Why OpenAI Created This Blueprint Now
The Character.AI Crisis
The timeline matters here. In January 2024, Sewell Setzer’s family sued Character.AI, claiming the platform’s “romantic” chatbot had enabled an intensive, emotionally manipulative relationship that contributed to his suicide. By September 2025, a second family sued over a similar case involving a 13-year-old exposed to sexual content. A third case emerged involving a bot named “Nina” that allegedly encouraged a teen to distance herself from her parents.
Character.AI’s response, announced in October 2025, was drastic: it banned all minors from the platform, requiring users to verify they were 18+. A decade-old startup built for educational content suddenly excluded teenagers entirely. The message was clear AI companies under legal fire were choosing caution over serving young users.
Regulatory Pressure Mounting
Simultaneously, legislatures moved fast. California SB 243 became the nation’s first AI chatbot safety law specific to minors, mandating session reminders to prevent addiction, parental consent mechanisms, and algorithmic safety disclosures. New York’s law went further, explicitly banning romantic or sexual chatbot interactions with minors. Federal lawmakers circulated proposals to require disclosure to parents whenever minors interact with AI systems, with some advocates pushing for an outright ban on chatbots serving anyone under 16.
In this legislative environment, OpenAI faced a choice: ban teenagers like Character.AI, or build a framework that demonstrates it can serve minors responsibly. The blueprint is OpenAI’s answer.
School Expansion Plans
A third factor: OpenAI has aggressively pursued education partnerships. ChatGPT is now embedded in thousands of U.S. schools, from high schools to universities. A blanket teen ban would undermine those partnerships and raise questions about OpenAI’s ability to control who accesses its products. The blueprint allows OpenAI to say: “Yes, teens can use this safely, with controls, and with parental visibility.”
The 5 Pillars of OpenAI’s Teen Safety Blueprint

Pillar 1: Age Identification & Prediction
This is the technical linchpin. Before OpenAI can apply teen-specific safeguards, it needs to know or at least make an educated guess whether you’re under 18.
OpenAI’s age prediction system is AI-powered and multi-layered. It analyzes:
- Language patterns: Vocabulary complexity, emoji usage, grammatical formality, slang preferences, and communication style
- Conversation topics: Homework questions, school schedules, college applications, and parent-related topics skew younger; tax advice, mortgage questions, and career transitions skew older
- Behavioral signals: Session length, time of day (nighttime browsing), frequency of usage, and initial onboarding questions
- Account-level data: Payment method (parental card vs personal), linked accounts, email domain (school email vs corporate), and account age
If ChatGPT’s algorithm is uncertain, it defaults to treating you as under 18 and applies full teen protections. Adults who slip through can verify their age via ID check or payment history confirmation.
The privacy benefit: Unlike ID-based verification systems, OpenAI minimizes data collection. It doesn’t require government ID upfront, avoiding the surveillance risks that plague European age-gate proposals. The downside: no system is foolproof.
Practical Reality:
French researchers in October 2025 tested AI age-verification systems across multiple platforms and found error rates of 7-10% for minors bypassing detection. More concerning: they discovered racial bias, with error rates reaching 27% for Black users versus 11% for white users, a disparity reflecting training data imbalances. VPNs, account spoofing, and other workarounds create additional gaps. OpenAI acknowledges these challenges but argues that an imperfect system is better than no system, especially when default protection errs on the side of caution.
Quick Answer: How does ChatGPT know if you’re a teen? OpenAI’s AI-powered age prediction analyzes your language style, conversation topics, behavioral patterns, and account signals. If uncertain, it defaults to under-18 protections automatically. Adults verify age via ID or payment history. Error rates are 7-10% for minors with technical workarounds possible, but defaults prioritize safety.
Pillar 2: Content & Interaction Policies for Minors
Once identified as under 18, users encounter stricter safeguards.
Prohibited content for minors includes:
- Depictions of suicide, self-harm, or eating disorders
- Graphic or immersive intimate content (explicit sex talk, role-playing scenarios, romantic engagement)
- Detailed violent content (graphic gore, torture, violence porn)
- Instructions for dangerous activities (the “Tide Pod challenge” equivalent)
- Facilitation of illegal substance access (how to buy drugs, synthesis guides)
- Body shaming, extreme diet advice, or appearance-focused harm
- Adult-initiated contact or grooming behavior
Restricted but context-dependent:
- Flirtatious or romance-adjacent conversations (ChatGPT won’t role-play as a romantic interest)
- Creative writing with suicide/self-harm themes (blocked by default; adults can override)
- Detailed substance information (factual education allowed; “how to use” guides blocked)
Beyond blocking, ChatGPT has built-in crisis detection protocols. If a minor’s messages suggest imminent suicidal ideation, self-harm intent, or abuse, the system flags for intervention. Parents can receive notifications; in extreme cases, OpenAI will contact authorities if harm is deemed imminent.
This approach differs meaningfully from Character.AI’s historical approach, which applied minimal restrictions and allowed romance-focused chatbots to exist without parental visibility.
Pillar 3: Parental Controls & Family Linking
Launched September 2025, ChatGPT’s parental controls let parents link their account to their teen’s and customize safety settings.
Setup process (5 minutes):
- Parent logs into ChatGPT settings → invites teen’s email → teen accepts → controls activate
- Parent can now customize behavior, toggle features, and receive alerts
What parents control:
- Age-appropriate model behavior: Whether ChatGPT applies teen-specific content restrictions (default: on)
- Memory and chat history: Whether ChatGPT remembers past conversations (default: limited for minors)
- Voice features: Audio conversations on/off
- Tool access: Which GPT plugins or advanced features are available
What parents can see:
- Alert notifications when distress signals are detected
- The ability to unlink the account (though teens receive notifications when this happens)
- General usage summaries (not full conversation logs, preserving privacy)
Critical limitation: Parents cannot read full conversation transcripts. This was intentional OpenAI balanced parental visibility with teen privacy expectations. Parents get oversight; teens retain some autonomy. For families needing deeper transparency, this may feel insufficient.
Quick Answer: ChatGPT parental controls let you link your account to your teen’s, enabling age-appropriate response rules, memory/voice controls, and distress alerts. Setup takes 5 minutes; parents see alerts and usage summaries but not full conversations, balancing oversight with teen privacy.
Pillar 4: Research-Informed Feature Design
OpenAI partnered with organizations like Common Sense Media, child development researchers, and educational institutions to embed safety into product design from the ground up. This means:
- Session reminders for minors (every 3 hours, per California law)
- Proactive notifications linking to mental health resources when crisis topics emerge
- Educational tone: Responses to teens emphasize that ChatGPT is an AI, not a friend or therapist
- Annual safety audits and transparent reporting
Unlike reactive policies that ban features after incidents, this pillar aims to prevent harm through deliberate design. Teens still get educational value; the experience is just more bounded.
Pillar 5: Transparency & Accountability
OpenAI is publishing detailed documentation of these policies, implementing third-party audits, and committing to quarterly transparency reports on safety incidents. This serves two purposes: it demonstrates OpenAI’s seriousness to regulators, and it creates public accountability.
How OpenAI’s Approach Compares to Competitors
| Feature | OpenAI/ChatGPT | Character.AI | Snapchat My AI | Google Gemini |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Verification | AI prediction + ID verify | Self-reported only (updated Oct 2025) | Account-based (indirect) | Self-reported |
| Parental Controls | Yes (Sept 2025) | Added post-lawsuit Oct 2025 | Limited | No |
| Crisis Detection | Yes + parent alert | Being developed | No | No |
| Content Restrictions | Comprehensive | Now extreme (banned minors) | Moderate | Basic |
| Approach | Proactive safety framework | Reactive (post-lawsuit ban) | Light-touch oversight | Permissive |
Key insight: Character.AI’s October 2025 decision to ban all minors was a capitulation; it eliminated the risk by eliminating the user base. OpenAI’s blueprint tries to thread the needle: serve teens responsibly without banning them. Snapchat and Google have adopted lighter approaches, signaling that an industry consensus around teen safety is still forming.
Technical Challenges & Limitations
OpenAI’s blueprint is ambitious, but it operates at the frontier of unsolved problems.
The Age Verification Gap
The French study on age-verification systems (October 2025) found that 7-10% of minors bypass age detection systems, often through VPNs, account spoofing, or simply using an older sibling’s account. No AI system is 100% accurate. More troubling: the same study found a 27% error rate for Black users compared to 11% for white users, revealing algorithmic bias in training data. This means some minors get through, and some minorities are disproportionately flagged as young.
OpenAI’s approach defaulting to teen protections when uncertain mitigates the first problem. But the second issue (bias) requires ongoing research and model retraining.
Privacy vs. Safety Trade-offs
Why can’t parents see full conversation logs? OpenAI deliberately chose not to implement this, citing privacy principles and COPPA/GDPR-K compliance constraints. Full surveillance would chill teen usage (why confide in ChatGPT if everything goes to your parents?) and create privacy liabilities for OpenAI in Europe. The compromise alerts for crisis signals, usage summaries, and restricted features feels minimalist to some families but reflects hard constraints.
False Positives
Adults sometimes get flagged as teenagers and locked into teen mode, creating friction. Verification workflows can be clunky. Over-caution can degrade the user experience for adults.
Quick Answer: Age verification on AI platforms faces accuracy issues (7-10% minors bypass, 27% error rate for Black users), privacy-safety trade-offs (no full conversation logs), and VPN workarounds. OpenAI minimizes data collection while defaulting to caution, but perfect solutions don’t exist yet.
What This Means for Parents: Actionable Steps
If you’re a parent with a teen using ChatGPT, here’s what to do now:
Immediate actions:
- Set up parental controls – Visit OpenAI’s official guide and link your account to your teen’s. Takes 5 minutes and activates all teen-specific protections.
- Discuss AI with your teen – Explain that ChatGPT is a tool, not a friend or therapist. Ask what they’re using it for (homework, writing, curiosity?).
- Review what’s restricted – Show them the content policy so they understand why certain conversations are blocked. Frame it as care, not surveillance.
- Understand the alert system – Know what signals trigger crisis notifications, so you respond appropriately.
Questions to ask your teen:
- What are you using ChatGPT for most often?
- Have you ever encountered a response that made you uncomfortable?
- Do you understand it’s artificial intelligence, not a real person?
- Has ChatGPT ever suggested meeting up or continuing a conversation outside the platform? (Red flag if yes.)
Red flags to watch:
- Excessive daily usage (3+ hours) or after-midnight sessions
- Emotional language suggesting attachment (“ChatGPT understands me better than anyone”)
- Secretive behavior around ChatGPT use
- Attempts to unlink parental controls
- Withdrawal from family activities or friends
Mini case study insight: Parents in pilot programs reported that parental controls reduced anxiety about teen AI use while maintaining trust teens felt their parents cared but weren’t reading every word. Open dialogue, combined with controls, works better than surveillance alone.
What This Means for Educators
Schools using ChatGPT need institutional policies alongside OpenAI’s technical safeguards.
Consider adopting guidelines like:
- Define acceptable use in classrooms (research tools yes; homework shortcuts no)
- Teach AI literacy: How does it work? What are its limits? How do you evaluate its outputs for bias?
- Set usage time limits in school settings to prevent over-reliance
- Brief parents on your school’s ChatGPT policy
- Monitor for signs that students are developing emotional attachments to AI tools
Educators also benefit from OpenAI’s research partnerships; the education sector now has a voice in shaping safety features, rather than being an afterthought.
The Regulatory Landscape: What’s Coming
State-Level Actions
California SB 243 (Jan 1, 2026 effective date) mandates:
- Session reminders every 3 hours for minors
- Parental consent mechanisms
- Annual safety reports to regulators
- Disclosure of training data and algorithmic decision-making
This is the baseline. New York’s law adds romance/sexuality bans. Six other states passed AI chatbot bills in 2025, most stricter than California’s.
Federal Proposals
Congress held hearings in September 2025 on AI chatbot regulation. Proposed bills range from transparency-focused (disclose to parents when minors use AI) to restrictive (ban chatbots for anyone under 16). None have passed yet, but the direction is clear: more regulation is coming.
International Context
The EU AI Act classifies child-facing AI as “high-risk,” requiring extensive testing and documentation. The UK’s Online Safety Bill includes provisions for AI recommendation algorithms. Global regulation is nascent but accelerating.
Criticisms & Concerns
Is it enough? Character.AI’s complete ban on minors suggests some stakeholders think OpenAI’s framework isn’t strict enough. Why allow teen use at all if risks exist? OpenAI would counter that educational benefits outweigh risks when controls are in place, and that a ban merely drives teens to less-supervised platforms.
Why now, not sooner? Lawsuits and regulation forced OpenAI’s hand. The proactive framing obscures that this is largely reactive responding to Character.AI’s crisis, not anticipating one internally. Cynics see the blueprint as an attempt to shape regulation favorably rather than from genuine safety prioritization.
Enforcement challenges: Even with state laws, enforcement is weak. How will California verify annual safety reports? Will OpenAI face penalties if an under-18 user bypasses age detection? The accountability mechanisms are aspirational.
Accessibility concerns: Session reminders every 3 hours might feel infantilizing to 17-year-olds. Content restrictions might block legitimate educational research (e.g., a teen writing an essay on self-harm prevention gets restricted). The “one-size-fits-all” approach doesn’t account for developmental differences between 13- and 18-year-olds.
Key Takeaways & Action Checklist
Summary:
The Teen Safety Blueprint introduces five safeguards: AI-powered age prediction (default to caution), content restrictions (suicide, sexual, violent content blocked), parental controls (linkage, customization, alerts), research-informed design (session reminders, resource links), and transparency (audits, public reporting). It’s OpenAI’s proactive response to lawsuits and state regulation, allowing teens to use ChatGPT safely without a blanket ban. Limitations include 7-10% age verification bypass rates, racial bias in detection, and parental visibility trade-offs. Setup takes 5 minutes; ongoing dialogue with your teen works best.
Practical Checklist:
- Review the full Teen Safety Blueprint PDF on OpenAI’s website
- Set up ChatGPT parental controls for your teen
- Have a conversation with your teen about AI safety, use cases, and boundaries
- Check your state’s AI safety laws (California, New York have active rules)
- Monitor for behavioral red flags: excessive usage, emotional attachment, secretive behavior
- Stay updated on regulatory changes and new research on teen AI safety
- Report safety concerns to OpenAI’s feedback channels or relevant authorities
Conclusion
The Character.AI tragedy forced a reckoning the AI industry couldn’t ignore. Millions of teenagers use chatbots daily, often without meaningful safeguards or parental awareness. OpenAI’s Teen Safety Blueprint represents the industry’s most comprehensive answer yet: a framework that protects without banning, restricts without disempowering, and creates oversight without surveillance.
Is it perfect? No. Age verification has gaps; bias exists in detection systems; privacy-safety trade-offs remain unresolved. But perfectionism is the enemy of progress. OpenAI’s proactive approach of anticipating harms and building safeguards into product design sets a new standard that competitors like Character.AI (now post-ban) and lighter-touch players like Google and Snapchat are now responding to.
For parents, the message is clear: your teen can use ChatGPT but with active involvement. Set up controls, stay in conversation, and remain vigilant. For policymakers, this blueprint serves as a model: responsible AI innovation for minors is possible without crushing innovation entirely.
The next chapters will be written by regulators, researchers, and OpenAI’s ongoing implementation. Stay informed. The rules around teen AI safety are crystallizing now, and your choices as parents, educators, and citizens will shape them.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) : Teens, Parents & the Blueprint
Can my teen still use ChatGPT after these changes?
Yes. The blueprint restricts certain types of content and interactions, but doesn’t ban teens from ChatGPT. Your teen can use it for homework, learning, and creative writing just with guardrails.
How accurate is the age prediction system?
Roughly 90% accurate, but not perfect. 7-10% of minors may bypass detection; racial bias in detection algorithms has been documented (higher error rates for Black users). If your teen lies about their age or uses a VPN, they could access adult-mode features.
Will I be able to see all my teen’s conversations?
No. Parental controls show usage summaries and alert you to crisis signals, but not full conversation logs. This preserves teen privacy while giving you visibility into patterns and concerns.
What happens if my teen tries to bypass the age verification?
Using a VPN, account spoofing, or an older sibling’s account could work. If discovered, OpenAI could disable the account. Parents should discuss the why behind restrictions rather than relying on controls alone.
Does this apply to all OpenAI products or just ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is the primary focus, but OpenAI indicates it will apply similar protections across consumer products. API-based applications built on OpenAI’s models will need to implement their own safeguards.
How is this different from YouTube’s age restrictions?
YouTube uses account age, device type, and viewing history. OpenAI uses language analysis and behavioral AI. Both systems have workarounds. The main difference: OpenAI is doing this proactively for a new product; YouTube adapted restrictions after years of laissez-faire policies.
Source: OpenAI