Xiaomi is doubling down on self-developed technology in 2026, with plans to expand its in-house chipset lineup, build a proprietary operating system, and develop AI large language models. The announcement came during an internal award ceremony where Xiaomi President Lei Jun revealed a 200 billion yuan ($27.7 billion) R&D investment commitment over the next five years, signaling the company’s ambition to become “the Apple of the Android world“.
What’s New in Xiaomi’s 2026 Strategy
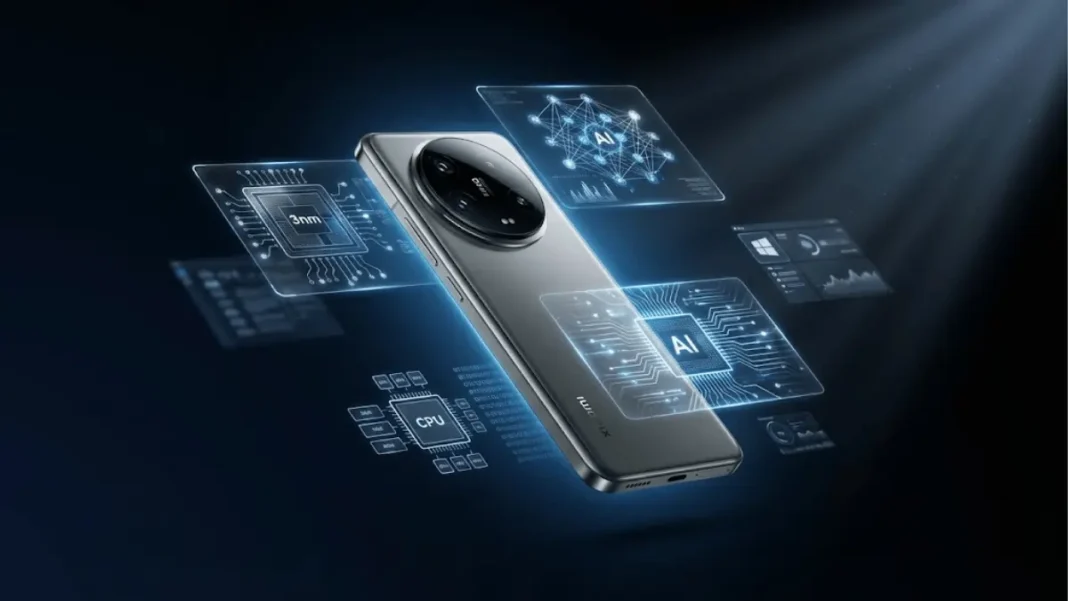
Xiaomi held an internal awards ceremony in early January 2026 where it reviewed 154 projects across 10 departments, covering AI, chipsets, imaging, and more. The XRING O1 chipset team received top honors for delivering Xiaomi’s first mainstream 3nm flagship processor.
Lei Jun confirmed three major technology initiatives for 2026:
- More self-developed chipsets following the success of XRING O1
- Proprietary operating system to reduce dependence on third-party platforms
- In-house AI large language models to power on-device intelligence
The company has already spent approximately 105 billion yuan ($14.5 billion) on in-house tech R&D over the past five years. The new 200 billion yuan commitment represents nearly double that investment, spread across the next half-decade.
Why the XRING O1 Chipset Matters
The XRING O1 chipset stands as Xiaomi’s breakthrough achievement in semiconductor development. Built on TSMC’s second-generation 3nm N3E process technology, the chip packs 19 billion transistors and features a 10-core CPU architecture.
Performance benchmarks show the XRING O1 competing with and in some cases surpassing Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite and MediaTek’s Dimensity 9400 processors. The chip’s CPU configuration includes:
- 2x Cortex-X925 cores at 3.9 GHz (performance)
- 4x Cortex-A725 cores at 3.4 GHz (balanced)
- 2x Cortex-A725 cores at 1.9 GHz (efficiency)
- 2x Cortex-A520 cores at 1.8 GHz (ultra-efficiency)
The XRING O1 also features a 16-core Immortalis-G925 GPU and a 6-core NPU for AI workloads. The 3nm process node delivers approximately 20% better power efficiency compared to 4nm alternatives.
Xiaomi became the first major mainland China brand to release a 3nm flagship processor, putting it in the same manufacturing tier as Apple, Qualcomm, and MediaTek.
What This Means for Users and the Industry
Xiaomi’s vertical integration strategy mirrors Apple’s successful model of controlling both hardware and software. By developing its own chips, operating system, and AI models, Xiaomi can:
- Optimize performance and battery life across its ecosystem
- Reduce component costs and supply chain dependence
- Differentiate its products from competitors using generic solutions
- Accelerate feature development without waiting for third-party updates
The move addresses a critical vulnerability in Xiaomi’s business model. Most Android manufacturers rely on Qualcomm or MediaTek for processors, Google for the operating system, and various partners for AI capabilities. Xiaomi’s 2026 roadmap aims to eliminate these dependencies.
For consumers, this could translate to faster software updates, better device optimization, and unique features unavailable on competing Android phones. The company’s Surge OS platform has already begun rolling out with integrated AI features including on-device text-to-image generation, AI portrait tools, and live subtitles.
Beyond Smartphones: Auto and IoT Expansion
While the 2026 roadmap focuses heavily on in-house technology development, Xiaomi continues expanding its automotive division. The company delivered over 410,000 vehicles in 2025 and has set a target of 550,000 units for 2026.
Xiaomi’s YU7 SUV model achieved over 150,000 deliveries within six months of launch 2.3 times the initial delivery volume of its SU7 sedan. The automaker plans to launch four new vehicles in 2026, including a refreshed SU7, an executive SU7 variant, and two extended-range SUVs.
On the broader IoT front, Xiaomi’s India division confirmed plans for an aggressive 2026 product push spanning smartphones priced from ₹7,000 to flagship devices, plus tablets, wearables, robot vacuum cleaners, and air purifiers. Senior Vice President Adam Zeng stated the company remains “very excited” about international markets during his maiden India visit.
What’s Next for Xiaomi’s Tech Stack
The timeline for Xiaomi’s proprietary OS and AI models remains unclear. The company has been testing its MiMo-V2-Flash large language model, with the free public testing period extended until January 20, 2026.
Industry observers expect Xiaomi to gradually introduce these technologies throughout 2026 rather than a single launch event. The XRING O1 chipset currently powers the Xiaomi 15S Pro in China, but broader rollout to mid-range and budget devices could take months.
Key questions remain unanswered:
- Will the new OS replace Android entirely or run as a fork?
- How will Xiaomi’s AI models compare to ChatGPT, Gemini, or other established platforms?
- Can the company maintain this R&D spending level if smartphone sales decline?
- Will U.S. export restrictions impact access to TSMC’s 3nm manufacturing?
Xiaomi has not provided official timelines for mass-market availability of its self-developed OS or AI models beyond confirming they are 2026 priorities.
Featured Snippet Boxes
What is Xiaomi’s XRING O1 chipset?
The XRING O1 is Xiaomi’s first in-house smartphone processor, built on TSMC’s 3nm technology with 19 billion transistors. It features a 10-core CPU, 16-core GPU, and 6-core NPU, competing directly with Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite and MediaTek Dimensity 9400.
How much is Xiaomi investing in R&D?
Xiaomi will invest at least 200 billion yuan ($27.7 billion) in research and development over the next five years, focusing on self-developed chips, operating systems, and AI models. This follows 105 billion yuan spent in the previous five years.
Is Xiaomi building its own operating system?
Yes, Xiaomi confirmed it is developing a proprietary operating system as part of its 2026 roadmap, though specific launch dates and technical details have not been disclosed. The company already offers Surge OS with AI features on select devices.
Why does Xiaomi want to make its own chips?
Creating in-house processors allows Xiaomi to reduce costs, control supply chains, optimize hardware-software integration, and differentiate from competitors. The strategy mirrors Apple’s successful model and reduces dependence on Qualcomm and MediaTek.