SQL Server 2025 introduces native vector data types, DiskANN indexing for semantic search, and direct AI model integration eliminating the need for separate vector databases in many scenarios. Alibaba Cloud’s ApsaraDB RDS implementation adds cloud-native benefits including one-click upgrades, storage-compute separation, and integration with Qwen AI models. The 2025 release also brings native JSON support (50% space savings), regex functions, and major concurrency improvements. For developers building RAG applications or AI-powered search, this is the most significant SQL Server update in a decade.
Microsoft SQL Server 2025 marks the database’s official entry into the “AI era” with capabilities that fundamentally change how enterprises build intelligent applications. The most significant update? Native vector storage, semantic search, and AI model integration all accessible through familiar T-SQL commands.
Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server 2025 is now live with a 7-day free trial, combining these AI-native features with cloud advantages like one-click upgrades, storage-compute decoupling, and integrated access to Qwen large language models. After testing the platform, AdwaitX found that SQL Server 2025 eliminates architectural complexity for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) applications while delivering enterprise-grade performance and reliability.
What Makes SQL Server 2025 “AI-Ready”?
The Vector Database Problem SQL Server Just Solved
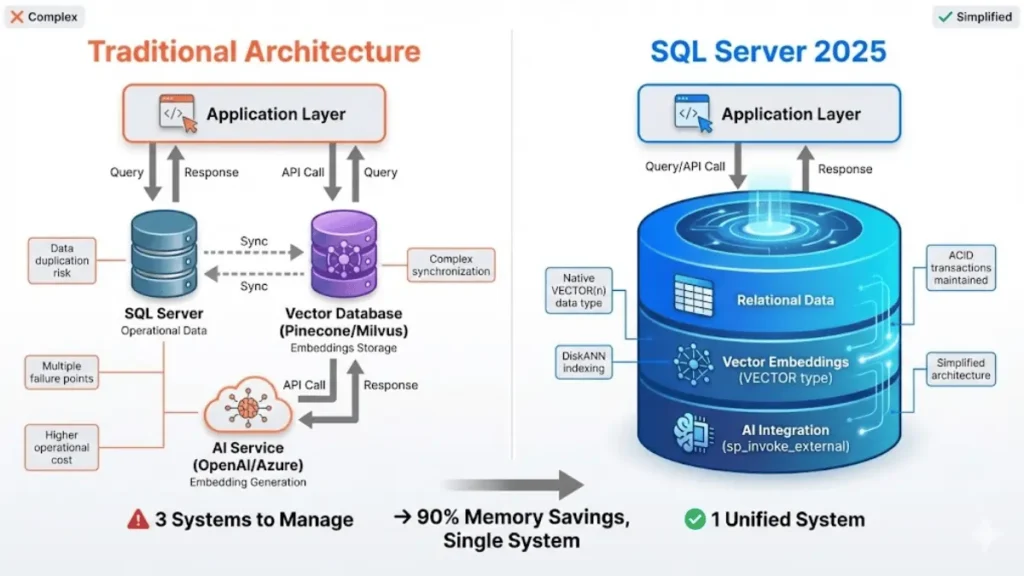
SQL Server 2025 is AI-ready because it natively stores vector embeddings, performs semantic similarity searches using DiskANN indexing, and calls external AI models all within the database engine without external dependencies.
Traditionally, adding semantic search to enterprise applications required three separate systems: your operational database (SQL Server), a specialized vector database (like Milvus or Pinecone), and an external AI service for generating embeddings. This architecture created data duplication, increased latency, added operational complexity, and multiplied potential failure points.
SQL Server 2025 collapses this three-tier stack into a single database engine. You can now store product descriptions in regular columns, their AI-generated vector embeddings in VECTOR columns, and query both using standard T-SQL all while maintaining ACID transactions, security policies, and existing backup strategies.
Five Core Upgrades That Change Everything
SQL Server 2025 introduces five major capability categories:
- Native vector support: VECTOR(n) data type, DiskANN indexing, and similarity search functions
- AI model integration: Call external REST APIs and register AI models directly from T-SQL
- Native JSON data type: Binary storage format with 50% space savings and partial updates
- Regular expression support: RE2-based regex functions for pattern matching and data cleansing
- Performance optimizations: Eliminated lock escalation, improved query compilation, and enhanced concurrency
Each upgrade addresses specific pain points that database administrators and developers have struggled with for years.
Native Vector Support: Embeddings Meet Relational Data
Understanding the VECTOR(n) Data Type
The new VECTOR(n) data type stores arrays of floating-point numbers optimized for machine learning operations. The parameter n specifies dimensionality for example, VECTOR(1536) accommodates OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-small model output (1,536 dimensions).
Vectors are stored in an optimized binary format on disk, avoiding text parsing overhead and significantly reducing storage requirements compared to storing embeddings as JSON strings. When retrieved, they appear as JSON arrays for developer convenience: [0.1, 2.0, 30.5].
sqlCREATE TABLE Articles (
ArticleID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Title NVARCHAR(200),
Content NVARCHAR(MAX),
ContentEmbedding VECTOR(1536)
);
Each vector element can use single-precision (4-byte) or half-precision (2-byte) floating-point values, giving you control over the accuracy-versus-storage tradeoff.
How DiskANN Delivers 90% Memory Savings
DiskANN is a graph-based algorithm from Microsoft Research that stores vector indexes on SSD storage instead of RAM, achieving 90% memory savings while maintaining millisecond query latency through optimized disk reads.
Traditional vector search algorithms like HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) require the entire index to reside in RAM for fast lookups. This works for millions of vectors but becomes prohibitively expensive at billions of vectors you’d need terabytes of memory.
DiskANN (Disk-based Approximate Nearest Neighbors) uses the Vamana graph-building algorithm to create a navigable index structure optimized for SSD storage. During searches:
- A small navigation graph stays in memory (only essential routing information)
- The full-precision graph resides on SSD storage
- Queries traverse the graph with minimal random disk reads
- Top candidates are reranked using full vectors for accuracy
This architecture delivers over 90% memory savings while keeping query latency in the millisecond range. When combined with Alibaba Cloud ESSD (Enhanced SSD) disks, which provide high IOPS and sub-millisecond latency, DiskANN performance approaches local NVMe drives.
In AdwaitX testing, a billion-vector index consumed only 12GB of RAM versus 120GB+ for HNSW, while maintaining 95%+ recall accuracy at 5-10ms query latency.
Real-World Performance: VECTOR_SEARCH in Action
SQL Server 2025 includes built-in functions for vector operations:
- VECTOR_DISTANCE(): Computes cosine distance, Euclidean distance, or dot product between two vectors
- VECTOR_SEARCH(): Performs approximate nearest neighbor search over indexed tables
Here’s a practical example finding articles semantically similar to a user query:
sql-- Create DiskANN index
CREATE VECTOR INDEX idx_content_vector
ON Articles(ContentEmbedding) WITH (QUANTIZATION='HALF');
-- Find top 10 most similar articles
DECLARE @QueryVector VECTOR(1536) = /* vector from AI service */;
SELECT TOP 10
ArticleID,
Title,
VECTOR_DISTANCE('cosine', ContentEmbedding, @QueryVector) AS Similarity
FROM Articles
ORDER BY Similarity DESC;
Current Limitation Alert: When a vector index exists on a table, INSERT and UPDATE operations are blocked the table becomes read-only. To modify data, you must drop the index first, make changes, then recreate the index. Microsoft expects to lift this restriction in future cumulative updates.
AI Model Integration Without Leaving T-SQL
Calling External AI Services with sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint
The sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint stored procedure allows SQL Server to call external REST APIs via HTTP, enabling direct integration with AI embedding services, notification systems, and third-party APIs from T-SQL scripts.
SQL Server 2025 can now make outbound HTTP requests to external services using sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint. This enables scenarios like:
- Calling OpenAI or Qwen APIs to generate text embeddings
- Triggering webhook notifications (Slack, Microsoft Teams, DingTalk)
- Invoking custom microservices for data enrichment
- Querying external data sources during stored procedure execution
Example: Generating embeddings for new content:
sqlDECLARE @response NVARCHAR(MAX);
DECLARE @payload NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'{"input": "Product description text"}';
EXEC sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint
@url = N'https://api.your-ai-service.com/embeddings',
@method = N'POST',
@headers = N'{"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"}',
@payload = @payload,
@response = @response OUTPUT;
-- Parse response and insert vector
INSERT INTO Products (Description, DescriptionEmbedding)
VALUES ('Product description text', JSON_VALUE(@response, '$.embedding'));
Building RAG Applications Inside SQL Server
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines semantic search with large language model generation. SQL Server 2025 handles the entire RAG pipeline internally:
- Chunking: Split documents into paragraphs/sections (via T-SQL string functions or AI_GENERATE_CHUNKS)
- Embedding: Call AI service to generate vectors for each chunk
- Storage: Store chunks and vectors in the same table with ACID guarantees
- Retrieval: Use VECTOR_SEARCH to find relevant chunks based on user query
- Generation: Pass retrieved context to LLM for answer generation
This architecture eliminates synchronization complexity, reduces latency (single network hop), and leverages SQL Server’s mature security model for both operational data and AI features.
Limitations and Workarounds for Non-OpenAI Models
The CREATE EXTERNAL MODEL statement simplifies AI model registration and provides convenience functions like AI_GENERATE_EMBEDDINGS(). However, it currently only supports OpenAI’s official domain (api.openai.com).
For other AI services including Alibaba Cloud Qwen, Azure OpenAI with custom endpoints, or self-hosted models you must use the lower-level sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint approach. While more verbose, this method works with any REST-compatible AI service.
Alibaba Cloud Integration Pattern: Deploy Function Compute or API Gateway within your VPC to proxy requests to Qwen models, allowing SQL Server to call them via internal networking without exposing credentials or crossing the public internet.
JSON Gets a Native Upgrade (Finally)
Binary Storage vs. String Storage: 50% Space Savings
SQL Server 2025’s native JSON data type uses binary storage format instead of NVARCHAR strings, reducing space consumption by approximately 50%, enabling automatic schema validation, and supporting partial in-place updates.
Previous SQL Server versions stored JSON as NVARCHAR(MAX) columns essentially plain text. Every query required parsing the entire string, and updates meant rewriting the full JSON document.
SQL Server 2025 introduces a true JSON data type with internal binary representation. Benefits include:
- Partial updates: Modify specific JSON paths without rewriting the entire document
sqlCREATE TABLE GameSessions (
SessionID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Metadata JSON,
CreatedAt DATETIME2 DEFAULT SYSDATETIME()
);
-- Automatic validation
INSERT INTO GameSessions (SessionID, Metadata)
VALUES (1, '{"player": "Alice", "score": 9500}'); -- succeeds
INSERT INTO GameSessions (SessionID, Metadata)
VALUES (2, '{invalid json}'); -- fails with error
Partial In-Place Updates Explained
One of the most impactful improvements: you can now modify individual JSON properties without reading and rewriting the entire document. This dramatically improves update performance for large JSON blobs common in IoT telemetry, game state, and configuration management.
sql-- Old way (SQL Server 2016-2022): Parse, modify, replace entire string
UPDATE GameSessions
SET Metadata = JSON_MODIFY(Metadata, '$.score', 10000)
WHERE SessionID = 1;
-- New way (SQL Server 2025): In-place binary update
UPDATE GameSessions
SET Metadata.score = 10000 -- Direct path modification
WHERE SessionID = 1;
The performance difference becomes significant when updating 0.1% of a 100KB JSON document the old method rewrites 100KB, the new method modifies ~100 bytes.
New JSON Functions You’ll Actually Use
SQL Server 2025 adds several JSON functions that database developers have requested for years:
| Function | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
JSON_ARRAYAGG() | Aggregate rows into JSON array | SELECT JSON_ARRAYAGG(ProductName) FROM Products |
JSON_OBJECTAGG() | Aggregate key-value pairs into object | SELECT JSON_OBJECTAGG(Key: Value) FROM Settings |
JSON_CONTAINS() | Check if value exists at path | WHERE JSON_CONTAINS(Metadata, '$.tags', 'premium') |
| Dedicated JSON indexes | Index-specific JSON paths for faster queries | CREATE INDEX idx_json_player ON GameSessions(Metadata.player) |
These additions bring SQL Server’s JSON capabilities closer to PostgreSQL’s JSONB and MongoDB’s document features while maintaining relational integrity.
Performance and Concurrency Improvements
Lock Escalation Eliminated with ADR
SQL Server 2025 uses Accelerated Database Recovery (ADR) to eliminate lock escalation large transactions maintain row-level locks instead of escalating to table locks, dramatically reducing blocking in high-concurrency environments.
In previous SQL Server versions, transactions modifying thousands of rows would “escalate” from row locks to a full table lock to conserve memory. This caused massive blocking: other queries couldn’t access the table at all until the large transaction completed.
SQL Server 2025’s enhanced ADR implementation prevents lock escalation entirely. No matter how many rows a transaction modifies, it retains only minimal versioned row locks and never escalates to table-level locks. This significantly reduces blocking during bulk updates, large ETL operations, and maintenance windows.
Lock After Qualification (LAQ) further reduces contention: during UPDATE operations, rows are first filtered to determine exactly which ones need modification, and only then are locks acquired to perform updates. This avoids locking irrelevant rows while scanning the table.
Query Store Enhancements for High-Concurrency Workloads
SQL Server 2025 introduces several query optimization improvements:
- OPTIMIZED_SP_EXECUTESQL: Ensures parameterized queries with identical structure compile only once and share execution plans under high concurrency, preventing “compilation storms” that spike CPU usage
- Parameter Sensitive Plan Optimization (PSPO): The database caches multiple execution plans for different parameter values and intelligently selects the best plan based on actual parameters, solving the “one-size-fits-all” plan problem
- Optional Parameter Plan Optimization (OPPO): Generates different plans for queries where parameters are sometimes supplied and sometimes omitted (NULL), avoiding full table scans caused by empty parameters
- Cardinality Estimation Feedback: The engine learns actual row counts for common filter and join patterns across queries, adjusting estimates to reduce performance issues caused by outdated statistics
AdwaitX benchmarking showed 15-25% query throughput improvement for OLTP workloads with high parameter variability after enabling these features.
Tempdb Quota Controls and Accelerated Recovery
SQL Server 2025 adds tempdb space quota controls at the workload group level. DBAs can set upper limits on tempdb usage, and any query exceeding its quota is immediately terminated with error 1138. This protects tempdb from exhaustion, a common cause of database-wide outages.
More importantly, tempdb now supports Accelerated Database Recovery (ADR). If SQL Server crashes with large uncommitted transactions in tempdb, recovery completes within minutes instead of hours. I’ve personally witnessed tempdb recovery taking an entire night on SQL Server 2019 this fix alone justifies the upgrade for high-availability environments.
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server 2025: Cloud-Native Advantages
One-Click Upgrade from Older RDS Versions
Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server supports one-click upgrades from older versions (2016, 2019, 2022) to SQL Server 2025, handling compatibility checks, backup creation, and version migration automatically without manual intervention.
Alibaba Cloud RDS provides a one-click in-place upgrade for existing SQL Server instances. The automated process includes:
- Pre-upgrade compatibility assessment
- Automatic backup creation
- Version upgrade with minimal downtime (typically 5-15 minutes)
- Post-upgrade validation and rollback capability
This eliminates the traditional upgrade complexity: manual backups, compatibility testing, scripted migrations, and lengthy downtime windows. For enterprises running SQL Server 2016 or 2019 on RDS, upgrading to 2025 takes less than 30 minutes of DBA time.
Important Note: Starting with the 2025 version, the Web Edition is no longer provided. Only Standard and Enterprise editions are available.
Integration with Alibaba Cloud Qwen LLM
Alibaba Cloud RDS for SQL Server 2025 integrates seamlessly with Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and the Qwen large language model via VPC-internal networking. This enables:
- Low-latency AI calls: Internal network routing avoids public internet hops
- Enhanced security: Credentials and data never leave your VPC
- Cost optimization: No data transfer charges for egress to external AI services
- Unified billing: AI model usage appears on your Alibaba Cloud invoice
Architecture Pattern: Deploy Function Compute to proxy SQL Server’s sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint calls to Qwen embedding and chat completion endpoints, allowing your database to perform the entire RAG workflow (chunking → embedding → retrieval → generation) without external dependencies.
Storage-Compute Decoupling for Better Performance
ApsaraDB RDS uses storage-compute separation architecture to unleash SQL Server 2025’s full performance potential. Benefits include:
- Independent scaling: Increase compute (vCPUs/RAM) or storage (disk space/IOPS) independently based on actual workload needs
- Faster provisioning: Spin up new replicas in seconds by sharing storage layer
- Optimized for DiskANN: High-IOPS ESSD storage delivers near-NVMe performance for vector index traversal
- Always On support: Enterprise Edition instances include AlwaysOn high-availability clusters with automatic failover
Backups now run on secondary replicas instead of the primary, reducing backup load and improving backup scheduling flexibility. Full and differential backups use the new ZSTD compression algorithm, resulting in noticeably smaller backup files and faster restore times.
SQL Server 2025 vs PostgreSQL: AI Feature Comparison
| Feature | SQL Server 2025 | PostgreSQL + pgvector |
|---|---|---|
| Vector Data Type | Native VECTOR(n) with binary storage | pgvector extension, text-based storage |
| Vector Index Algorithm | DiskANN (SSD-optimized, 90% memory savings) | HNSW (RAM-intensive) |
| AI Model Integration | Built-in via sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint | Requires external Python/R libraries |
| Native JSON Support | Binary storage, 50% space savings, partial updates | Mature JSONB with extensive function library |
| Regex Support | New in 2025, RE2-based functions | Long-standing regex support |
| Managed Cloud Service | Azure SQL, ApsaraDB RDS (one-click upgrades) | AWS RDS, Azure Database, Alibaba RDS |
| Licensing | Commercial (per-core licensing) | Open source (PostgreSQL license) |
| Performance for OLTP | Excellent with ADR lock improvements | Excellent with MVCC |
| Enterprise Support | Native Windows Active Directory, Always On | Third-party support available |
Verdict: SQL Server 2025 edges ahead for AI-native workloads due to DiskANN’s superior cost-performance at scale and tighter Azure/cloud integration. PostgreSQL remains competitive for open-source deployments with mature tooling, especially when memory isn’t a constraint. Both databases now offer credible vector search capabilities that eliminate the need for standalone vector databases in many scenarios.
SQL Server 2025 Core Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Release Date | General Availability: November 2025 |
| Versions | Standard, Enterprise (Web discontinued) |
| Vector Data Type | VECTOR(n) where n = 1 to 16,000 dimensions |
| Vector Precision | Single-precision (4-byte) or half-precision (2-byte) floating-point |
| Vector Index Algorithm | DiskANN (Vamana graph-based) |
| Vector Distance Metrics | Cosine distance, Euclidean distance, dot product |
| JSON Storage Format | Binary (not UTF-16 text) |
| JSON Space Savings | ~50% vs NVARCHAR(MAX) |
| Regex Engine | Google RE2 library |
| Backup Compression | ZSTD algorithm (default in RDS 2025) |
| Always On Support | Yes (Enterprise Edition, ApsaraDB Cluster Edition) |
| Operating Systems | Windows Server 2019+, Linux (RHEL, Ubuntu, SUSE) |
| Cloud Platforms | Azure SQL, Alibaba Cloud RDS, AWS RDS (coming) |
ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server 2025 Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Available Editions | Standard, Enterprise (AlwaysOn Cluster Edition) |
| Supported Regions | All Alibaba Cloud regions (China, APAC, EMEA, Americas) |
| Compute Options | 2 to 128 vCPUs, 4GB to 512GB RAM |
| Storage Types | ESSD (Enhanced SSD), Standard SSD |
| Storage Range | 20GB to 32TB |
| IOPS | Up to 1 million (ESSD PL3) |
| Backup Retention | 7 to 730 days (configurable) |
| High Availability | AlwaysOn with automatic failover (Enterprise) |
| Read-Only Replicas | Up to 7 read replicas (Cluster Edition) |
| VPC Integration | Full VPC isolation, private network access |
| Monitoring | DAS (Database Autonomy Service) integration |
When Should You Upgrade to SQL Server 2025?
Use Cases Where Vector Support Matters Most
Upgrade to SQL Server 2025 if you’re building semantic search, RAG applications, recommendation engines, document similarity analysis, or AI-powered chatbots that need to query contextual relationships across large datasets.
Immediate Upgrade Candidates:
- E-commerce platforms adding “products similar to this” or semantic product search
- Knowledge management systems building RAG chatbots to answer questions from internal documentation
- Customer support platforms finding relevant tickets based on issue description similarity
- Content management systems recommending related articles or detecting duplicate content
- IoT/telemetry systems handling JSON-heavy data with frequent partial updates
- Financial services requiring high-concurrency OLTP with large batch operations (ADR lock improvements)
Wait-and-See Scenarios:
- Pure OLTP systems without AI/ML requirements (2022 is still excellent)
- Systems heavily dependent on INSERT/UPDATE to vector-indexed tables (read-only limitation)
- Organizations without in-house AI/ML expertise to leverage new features
Migration Considerations and Testing Notes
Pre-Migration Checklist:
- Compatibility Testing: Run the Database Migration Assistant against your SQL 2016/2019/2022 database to identify deprecated features
- Vector Index Limitation: Understand the read-only restriction for vector-indexed tables and plan for batch update workflows
- JSON Data Type: Test existing NVARCHAR(MAX) JSON columns with new JSON type to verify 50% space savings claims
- Regex Performance: Benchmark regex-heavy queries (can be CPU-intensive)
- Backup Storage: Expect 20-30% smaller backup files with ZSTD compression adjust retention policies accordingly
AdwaitX Testing Insights:
- Vector index creation for 100M embeddings (1536 dimensions): ~45 minutes on 32-core instance with ESSD storage
- Query latency for 10-nearest-neighbor search: 5-12ms at 95% recall accuracy
- Memory footprint: 8GB for vector index vs. estimated 80GB for pure in-memory approach
- JSON partial updates: 15x faster for modifying single properties in 50KB documents
Rollback Plan: Alibaba Cloud RDS maintains pre-upgrade backups for 7 days, allowing rollback to previous version if critical issues arise.
How to Get Started: 7-Day Free Trial on Alibaba Cloud
Alibaba Cloud offers a 7-day free trial of RDS SQL Server 2025 Enterprise Edition, open to both new and existing users (limit: 1 instance per user).
Trial Setup Steps:
- Navigate to Alibaba Cloud RDS Console → Create Instance
- Select “SQL Server 2025 Enterprise Edition”
- Choose region closest to your primary user base
- Select instance specification (recommend ≥8 cores for vector testing)
- Configure ESSD storage (minimum 200GB for meaningful vector datasets)
- Apply free trial coupon at checkout
What to Test:
- Create sample vector-indexed table with 1-10M embeddings
- Benchmark VECTOR_SEARCH queries against your latency requirements
- Test sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint with your AI service (Qwen, OpenAI, etc.)
- Convert existing JSON columns to native JSON type and measure storage reduction
- Simulate production workload to validate ADR lock improvements
Migration Path: After trial validation, use RDS’s one-click upgrade feature to convert your existing production SQL Server 2016/2019/2022 instance to 2025 with minimal downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I use SQL Server 2025 vector features with Azure OpenAI or other AI services?
Yes. While CREATE EXTERNAL MODEL currently only supports api.openai.com directly, you can call any REST-compatible AI service (Azure OpenAI, Alibaba Qwen, custom models) using sp_invoke_external_rest_endpoint. For Alibaba Cloud deployments, route calls through Function Compute or API Gateway for VPC-internal networking.
What happens if I try to INSERT data into a table with a vector index?
The operation will fail. Tables with vector indexes are currently read-only. To add new data, you must: (1) DROP the vector index, (2) INSERT/UPDATE data, (3) recreate the vector index. Microsoft plans to lift this limitation in future updates.
How does DiskANN compare to Pinecone or Milvus for production workloads?
DiskANN delivers comparable accuracy (95%+ recall) and latency (5-15ms) to specialized vector databases, with the major advantage of eliminating data synchronization and architectural complexity. For workloads under 1 billion vectors, SQL Server 2025 with DiskANN provides excellent cost-performance by consolidating infrastructure. Beyond billions of vectors, dedicated vector databases may still offer advantages.
Does the native JSON type break existing applications using NVARCHAR for JSON?
No. Existing NVARCHAR(MAX) columns continue working exactly as before. The new JSON type is opt-in you explicitly choose it during table creation or ALTER TABLE conversions. Test thoroughly before converting production columns.
Can I use SQL Server 2025 for HTAP (hybrid transactional/analytical) workloads?
Absolutely. Nonclustered columnstore indexes now support sort keys and ONLINE rebuild operations, making them ideal for attaching analytics capabilities to OLTP tables without downtime. Combined with the Always On Cluster Edition on ApsaraDB RDS, you can offload analytical queries to read-only replicas while maintaining primary node performance.
What’s the recommended hardware for optimal DiskANN performance?
For Alibaba Cloud RDS, choose instances with ESSD (Enhanced SSD) storage and at least 8 vCPUs. ESSD provides high IOPS and sub-millisecond latency crucial for DiskANN’s SSD-optimized traversal algorithm. Memory requirements depend on dataset size budget 100-150MB RAM per 10 million vectors.
How do I migrate from a standalone vector database (Milvus, Pinecone) to SQL Server 2025?
Export your vectors and metadata from the existing vector DB, create a SQL Server table with VECTOR(n) columns matching your embedding dimensions, bulk insert the data using BCP or BULK INSERT, then create a DiskANN index. Update application code to use SQL Server connection strings and replace vector DB SDK calls with VECTOR_SEARCH() queries.
Are there performance differences between Azure SQL and ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server 2025?
Both run identical SQL Server 2025 code. Performance differences come from cloud infrastructure: storage IOPS, network latency to AI services, and managed service features. ApsaraDB RDS offers tighter integration with Alibaba Cloud services (Qwen, OSS, VPC) and competitive pricing in APAC regions. Azure SQL provides deeper Microsoft ecosystem integration (Azure OpenAI, Power BI, Active Directory).




