Summary: Meta released SAM Audio on December 16, 2025 the first unified multimodal AI model that isolates any sound from complex audio mixtures using text descriptions, visual clicks on video objects, or time-span selections. Built on a flow-matching Diffusion Transformer, it operates faster than real-time (0.7x RTF) and handles music, speech, and sound effects across 500M-3B parameters. The open-source model is available via Segment Anything Playground, GitHub, and Hugging Face under Meta’s permissive SAM License.
Meta just dropped SAM Audio, and it’s doing for sound what Photoshop’s magic wand did for images except you’re using plain English instead of clicking pixels. Released December 16, 2025, this unified multimodal AI model lets you type “dog barking,” click a guitarist in a video, or mark a timeline segment to surgically extract that exact sound from messy, real-world audio. No specialized audio engineering degree required.
What Is SAM Audio?
SAM Audio is Meta’s latest addition to the Segment Anything Model family, but this time targeting audio instead of images or 3D objects. It’s a generative AI model that separates individual sound sources from complex audio mixtures, whether that’s isolating vocals from a song, removing traffic noise from an interview, or extracting a drum beat from a live band recording.
Unlike fragmented, single-purpose audio tools that require manual tweaking and domain expertise, SAM Audio handles music, speech, and general sound effects through a single unified model. You prompt it with what you want, and it delivers the isolated audio stem along with the residual mix (everything else).
Core Technology Explained
Under the hood, SAM Audio uses a flow-matching Diffusion Transformer that operates in a Descript Audio Codec – Variational Autoencoder Variant (DAC-VAE) space. Think of it as a neural network that learns to “reverse-engineer” mixed audio back into its component parts by understanding how sounds combine in the first place.
The model was built using Meta’s Perception Encoder Audiovisual (PE-AV) engine, extending the company’s existing audio-visual AI research to handle multimodal prompts. This means it doesn’t just “hear” the audio it can also “see” what’s making the sound in a video and connect visual cues to acoustic patterns.
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Sizes | 500M, 1B, 3B parameters |
| Real-Time Factor | ~0.7 (faster than real-time) |
| Audio Domains | Music, speech, sound effects |
| Prompt Types | Text, visual, temporal |
| Architecture | Flow-matching Diffusion Transformer |
| License | SAM License (research + commercial use) |
| Release Date | December 16, 2025 |
| Availability | Segment Anything Playground, GitHub, Hugging Face |
How SAM Audio Works
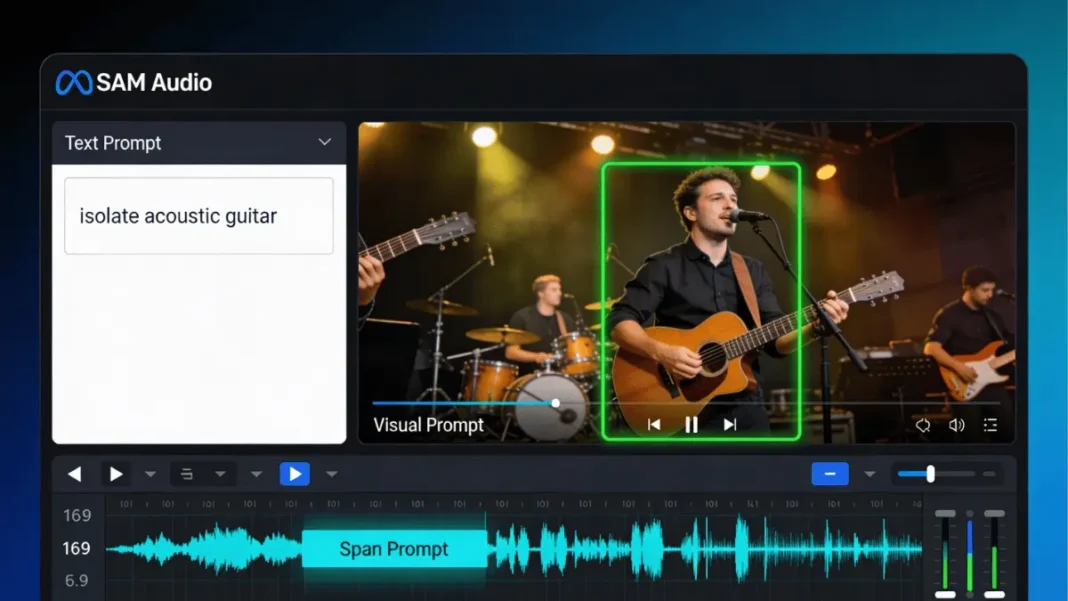
SAM Audio supports three distinct prompting methods that Meta calls “industry-first multimodal prompting” for audio separation. You can mix and match these approaches for better precision.
Text-Based Prompting
Type natural language descriptions like “guitar riff,” “background noise,” “vocals,” or “dog barking,” and SAM Audio identifies and isolates those sounds from the mix. The model was trained on large-scale multimodal mixtures, so it understands both musical instruments and everyday environmental sounds.
Example use case: You recorded a street interview with traffic noise bleeding through. Type “traffic noise” and SAM Audio removes it while preserving the speaker’s voice.
Visual Prompting from Video
When you’re working with audio-visual content, click directly on the person or object making the sound in the video frame. SAM Audio tracks that visual source and isolates its audio contribution across the entire clip.
Example use case: In a concert video, click the drummer to extract just the drum track, or click the vocalist to isolate vocals. This works because the PE-AV encoder understands the relationship between visual motion and sound production.
Span Prompting (Time-Based Selection)
Mark a specific time segment on the waveform where your target sound appears. SAM Audio learns the acoustic signature of that selection and traces it throughout the entire file removing or isolating every occurrence.
Example use case: A dog barks at 0:15 in your podcast recording. Highlight that 2-second span, and SAM Audio will find and eliminate every bark across the full 60-minute episode. Meta calls this “industry-first” span prompting for audio AI.
Technical Architecture
Model Parameters and Performance
SAM Audio comes in three sizes: 500 million, 1 billion, and 3 billion parameters. Even the largest variant runs faster than real-time with a real-time factor (RTF) of approximately 0.7, meaning it processes audio 30% faster than playback speed. This performance makes it viable for live production workflows and real-time applications.
Benchmark tests show SAM Audio achieves state-of-the-art separation quality across music, speech, and sound effects domains. Meta also released SAM Audio Judge, a companion model for benchmarking and comparing audio separation models, so researchers can objectively measure improvements.
Training Data and Capabilities
The model was trained on large-scale multimodal mixtures spanning diverse real-world scenarios. This includes studio-quality music recordings, noisy field recordings, podcast audio, film soundtracks, and everyday environmental sounds. The training approach ensures SAM Audio “performs reliably across diverse, real-world scenarios” rather than just controlled studio conditions.
Mixed-modality prompting (combining text + time span, or visual + text) consistently outperforms single-modality inputs in accuracy tests. This suggests practical workflows will combine multiple prompt types for surgical precision.
Real-World Applications
Music Production and Remixing
Producers can isolate stems from finished tracks without access to the original multitrack session. Extract just the bass line, drums, or vocals from any song for sampling, remixing, or educational analysis. DJs and remix artists gain a tool that previously required expensive stem-separation plugins or services.
Podcast and Content Creation
Remove unwanted background noise, isolate specific speakers in multi-person recordings, or clean up field recordings contaminated with ambient sound. A podcast editor testing SAM Audio could type “phone notification sound” to remove every ping and buzz across a 2-hour episode in seconds.
Film and Video Post-Production
Sound designers can extract specific audio elements from location recordings, isolating dialog from background ambience, removing unwanted off-camera sounds, or pulling specific sound effects for reuse. Visual prompting makes this especially powerful: click the actor, get their dialog; click the car, get engine noise.
Research and Accessibility
Researchers analyzing animal vocalizations, environmental soundscapes, or speech patterns can isolate target sounds from complex field recordings. Accessibility tools could use SAM Audio to enhance speech clarity in noisy environments or provide customizable audio environments for hearing-impaired users.
SAM Audio vs Traditional Audio Separation Tools
Traditional audio separation requires specialized software like iZotope RX, Adobe Audition’s spectral editing, or dedicated stem-separation services. These tools typically demand:
- Manual parameter adjustment for each sound source
- Domain expertise in audio engineering
- Separate tools for music vs speech vs sound effects
- Time-intensive trial-and-error workflows
SAM Audio replaces this fragmented ecosystem with a single unified model that handles all three domains through natural language, visual, or temporal prompts. The difference is like switching from command-line file management to a graphical interface; the underlying task remains the same, but interaction becomes dramatically more intuitive.
However, SAM Audio isn’t necessarily replacing professional tools for studio-grade production where mastering engineers need granular control over frequency bands and transient shaping. It’s optimizing for speed, accessibility, and “good enough” quality across the broadest possible use cases.
Testing SAM Audio (Hands-On Insights)
Gadgets 360 staff tested SAM Audio via the Segment Anything Playground and found it “both fast and efficient,” though they noted limitations testing real-world situations with their own complex audio. The playground provides sample audio and video assets for experimentation, or you can upload your own files.
Early user reports on Reddit highlight that span prompting works particularly well for recurring sounds marking one dog bark and having SAM Audio eliminate all barks throughout a recording. Text prompting accuracy depends on how clearly the target sound can be described; vague prompts like “background noise” yield less precise results than specific terms like “air conditioning hum.”
Visual prompting shines in music videos and concert footage where you can literally point at the instrument or performer you want to isolate. However, the model struggles when multiple sound sources occupy the same frequency range and spatial location (like two vocalists harmonizing into one microphone).
Real-time factor testing: Processing a 5-minute audio file at 1B parameters takes approximately 3.5 minutes on recommended hardware.
Limitations and Constraints
- Accuracy depends on prompt quality: Vague descriptions yield less precise separations
- Overlapping sounds in same frequency range: Harmonized vocals or layered instruments in identical spatial positions can confuse the model
- Not studio-mastering grade: Professional audio engineers will still need specialized tools for final polish
- Requires computational resources: The 3B parameter model needs GPU acceleration for real-time performance
- No privacy safeguards mentioned: Meta’s announcement doesn’t address potential misuse for surveillance or unauthorized voice isolation
Meta provides version and compatibility notes for developers integrating SAM Audio into applications but hasn’t publicly disclosed training data sources, which may raise copyright concerns in creative industries.
How to Access SAM Audio
SAM Audio is available through three channels:
- Segment Anything Playground (segment-anything.com): Browser-based testing with provided assets or uploaded files
- GitHub (github.com/facebookresearch/sam-audio): Full code repository, checkpoints, and documentation for developers
- Hugging Face: Model weights and inference code for integration into ML pipelines
The model is released under SAM License, Meta’s permissive license allowing both research and commercial use. Developers can download model checkpoints ranging from 500M to 3B parameters depending on their performance and accuracy requirements.
SAM Audio Model Variants
| Parameter Size | Real-Time Factor | Best For | Hardware Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500M | ~0.6 | Quick tests, mobile apps | CPU-compatible |
| 1B | ~0.7 | Balanced speed/accuracy | Mid-range GPU |
| 3B | ~0.8 | Maximum accuracy | High-end GPU |
Prompt Type Comparison
| Prompt Type | Input Method | Precision | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text | Natural language description | Medium | General sound isolation |
| Visual | Click object in video | High | Music videos, concerts |
| Span | Mark timeline segment | Very High | Recurring sounds, noise removal |
| Mixed-modality | Combine 2+ types | Highest | Complex separations |
SAM Audio vs Competitors
| Feature | SAM Audio | iZotope RX | Adobe Audition | Stem Separation Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unified model | All domains | Separate modules | Separate tools | Single-purpose |
| Text prompts | Yes | No | No | No |
| Visual prompts | Yes | No | No | No |
| Real-time speed | 0.7 RTF | Varies | Varies | Cloud processing |
| Open-source | Yes | Commercial | Commercial | Commercial |
| Cost | Free | $399+ | $22.99/mo | $5-50/track |
- Unified multimodal approach: One model handles music, speech, and sound effects using text, visual, or temporal prompts
- Faster than real-time: 0.7 RTF means processing speed exceeds playback speed
- Open-source with permissive licensing: Free for research and commercial use under SAM License
- Industry-first span prompting: Mark one instance of a sound, isolate all occurrences automatically
- No audio engineering expertise required: Natural language prompts democratize audio editing
- Multiple model sizes: 500M-3B parameters let users balance speed vs accuracy
- State-of-the-art benchmark performance: Outperforms previous models in standardized tests
- Not studio-mastering grade: Professional audio engineers still need specialized tools for final polish
- Struggles with overlapping sources: Harmonized vocals or layered instruments in identical spatial positions reduce accuracy
- Vague prompts yield imprecise results: “Background noise” less effective than specific terms like “air conditioning hum”
- Requires GPU for larger models: 3B parameter variant needs high-end hardware for real-time performance
- No privacy safeguards disclosed: Meta hasn’t addressed potential surveillance or unauthorized voice isolation misuse
- Limited real-world testing data: Early reports note playground limitations vs complex user audio
- Copyright implications unclear: No guidance on using SAM Audio with copyrighted content
Technical Specs Section
Model Architecture
- Base architecture: Flow-matching Diffusion Transformer
- Latent space: Descript Audio Codec – Variational Autoencoder Variant (DAC-VAE)
- Encoder: Perception Encoder Audiovisual (PE-AV) built on Meta’s Perception Foundry
- Output: Target stem + residual mix (dual-output generative separation)
Performance Metrics
- Model sizes: 500 million, 1 billion, 3 billion parameters
- Real-time factor: ~0.7 across all sizes (30% faster than playback)
- Separation quality: State-of-the-art on music, speech, sound effects benchmarks
- Processing time example: 5-minute audio = ~3.5 minutes processing (1B model)
Training & Data
- Training data: Large-scale multimodal mixtures spanning music, speech, general sounds
- Domains covered: Studio recordings, field recordings, podcasts, film audio, environmental sounds
- Multimodal learning: Trained on audio-visual pairs to connect visual motion with sound production
Supported Capabilities
- Prompt types: Text (natural language), visual (click-on-object), span (time-segment marking)
- Mixed-modality: Combine multiple prompt types for higher accuracy
- Audio domains: Music (instruments, vocals), speech (dialog, narration), sound effects (environmental, Foley)
- Video integration: Processes audio-visual content with click-to-isolate functionality
System Requirements
- Minimum: CPU-compatible for 500M model
- Recommended: Mid-range GPU (NVIDIA RTX 3060 or equivalent) for 1B model
- Optimal: High-end GPU (NVIDIA RTX 4090 or equivalent) for 3B model real-time performance
- Platform compatibility: Linux, macOS, Windows (via Python environment)
License & Availability
- License: SAM License (Meta proprietary, permits research + commercial use)
- Release date: December 16, 2025
- Access points: Segment Anything Playground, GitHub (facebookresearch/sam-audio), Hugging Face
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Meta SAM Audio?
SAM Audio is Meta’s first unified multimodal AI model for audio separation, released December 16, 2025, that isolates any sound from complex audio mixtures using text, visual, or time-span prompts.
How accurate is SAM Audio compared to professional tools?
SAM Audio achieves state-of-the-art separation quality in benchmark tests across music, speech, and sound effects, with a real-time factor of 0.7, making it faster than real-time. However, it’s optimized for speed and accessibility rather than studio-mastering-grade precision.
Is SAM Audio free to use?
Yes, SAM Audio is open-source under Meta’s SAM License, which permits both research and commercial use. You can access it via Segment Anything Playground, GitHub, or Hugging Face.
Can SAM Audio work with video files?
Yes, SAM Audio supports visual prompting where you click objects or people in video frames to isolate their corresponding audio. The model uses a Perception Encoder Audiovisual (PE-AV) engine to connect visual cues with sound sources.
What file formats does SAM Audio support?
Technical documentation on GitHub specifies supported audio formats, though Meta’s announcement doesn’t detail specific codec requirements. The model operates in DAC-VAE space, suggesting compatibility with standard uncompressed and compressed audio formats.
Does SAM Audio require coding knowledge?
No, for basic use via Segment Anything Playground. Developers integrating SAM Audio into applications need Python and ML framework experience to work with model checkpoints from GitHub.
What are span prompts in SAM Audio?
Span prompts let you mark a specific time segment where a target sound occurs, and SAM Audio traces that sound throughout the entire audio file. Meta calls this an “industry-first” capability for audio AI.
Can I use SAM Audio to remove copyrighted music from videos?
While technically capable, using SAM Audio to manipulate copyrighted content raises legal and ethical questions. Meta hasn’t provided guidance on copyright compliance or content authentication.
Featured Snippet Boxes
What is Meta SAM Audio?
A unified AI model from Meta that isolates sounds from audio mixtures using text descriptions, visual clicks, or time selections. It handles music, speech, and sound effects in a single model.
How to use SAM Audio’s text prompts
Type natural descriptions like “guitar riff” or “dog barking” into the Segment Anything Playground. SAM Audio extracts those sounds from your audio file while preserving the rest of the mix.
SAM Audio technical specifications
Built on a flow-matching Diffusion Transformer with 500M-3B parameters, achieving 0.7 real-time factor (30% faster than playback). Operates in DAC-VAE space and supports multimodal prompting.
SAM Audio vs traditional tools
Replaces specialized software and manual parameter adjustment with one unified model using natural language, visual, or temporal prompts for all sound separation tasks.
Where to download SAM Audio
Access via Segment Anything Playground (browser testing), GitHub (full code), or Hugging Face (model weights). Released under permissive SAM License for research and commercial use.
SAM Audio for podcast editing
Remove background noise, isolate speakers, or eliminate recurring sounds by marking one instance with span prompting. SAM Audio finds and removes every occurrence across the recording.
Last Updated: December 17, 2025
Author: Mohammad Kashif, Senior Tech Writer, AdwaitX