Summary: AI agents are no longer futuristic concepts; they’re autonomous digital workers reshaping how enterprises operate right now. According to Google Cloud’s newly released 2026 AI Agent Trends Report, these intelligent systems can understand goals, develop multi-step plans, and execute actions with minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional chatbots that simply respond to queries, AI agents actively collaborate, make decisions, and optimize workflows across entire organizations.
AI agents are autonomous software systems powered by LLMs that analyze data, make decisions, and execute multi-step actions to achieve business goals without constant human oversight. Unlike chatbots, they maintain contextual memory, adapt to changing conditions, and collaborate with other systems.
What Are AI Agents and Why 2026 Matters
AI agents are software systems powered by large language models (LLMs), contextual embeddings, and machine learning that autonomously analyze data, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. They maintain memory of previous interactions, track customer history through timeline views, and execute multi-step workflows across systems like CRM platforms, DevOps tools, and support applications.
AI Agents vs Traditional Chatbots
The distinction between chatbots and AI agents lies in autonomy and capability. Chatbots follow pre-scripted rules for repetitive, low-complexity tasks like answering FAQs or checking order status. AI agents, however, leverage decision-making models to prioritize requests, update records in real-time, and escalate issues based on severity with minimal human intervention.
| Feature | Traditional Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Rule-based, scripted | Autonomous, context-aware |
| Task Complexity | Single-step queries | Multi-step workflows |
| Learning Capability | Fixed responses | Adapts from interactions |
| System Integration | Limited APIs | Cross-platform orchestration |
| Memory | Session-based only | Persistent context tracking |
| Use Case | FAQs, basic support | Complex problem-solving, automation |
While 98% of what companies currently call “AI agents” are actually structured document retrieval systems, true agents possess both intelligence and autonomous execution capability.
The Shift from Copilots to Autonomous Agents
Enterprises are transitioning from generalized AI copilots to targeted, role-based agents grounded in enterprise data and trained for domain-specific outcomes. IDC forecasts that by 2026, AI copilots will integrate into 80% of enterprise workplace applications, but the real transformation comes from specialized agents that work inside Teams, Asana, Jira, and Notion. Microsoft 365 Copilot’s Analyst and Researcher agents exemplify this evolution toward AI that functions where work actually happens.
Enhanced Productivity Through Task Delegation
AI agents are delivering measurable productivity gains by taking over time-consuming, repetitive work. Google Cloud’s research shows that agents can save workers 40+ minutes per interaction by automating routine tasks like data entry, report generation, and scheduling.
Real-World Impact: Telus and Suzano Case Studies
Telus, a Canadian telecommunications giant, deployed AI agents to optimize call routing and provide real-time guidance to customer service representatives. The agents analyze customer sentiment mid-conversation, surface relevant knowledge base articles, and recommend next-best actions reducing average handling time by 23%.
Suzano, a Brazilian pulp and paper manufacturer, implemented AI agents to monitor equipment sensors and predict maintenance needs. The agents autonomously schedule repairs, order replacement parts, and notify technicians preventing 15% of potential production downtime.
How Agents Free Up Strategic Time
AI agents handle what MIT researchers call “cognitive offloading” mundane tasks that consume mental bandwidth but add little strategic value. By automating meeting summaries, email triage, expense report processing, and data lookups, agents allow knowledge workers to focus on creative problem-solving, relationship-building, and innovation.
AI agents boost productivity by automating repetitive tasks like data entry, scheduling, and report generation. Enterprise deployments show time savings of 40+ minutes per interaction, with Telus reducing call handling time by 23% through agent-assisted customer service.
Multi-Agent Workflows Automate Business Processes
The breakthrough in 2026 isn’t single agents it’s orchestrated teams of specialized agents working together through agentic workflows. These multi-agent systems coordinate across departments, applications, and data sources to complete end-to-end business processes.
Understanding Agentic Workflows
Agentic workflows divide complex business processes into discrete tasks, assigning each to the most capable specialized agent. Think of it like a relay race: a lead qualification agent identifies promising prospects, passes them to a discovery agent that the research company needs, which then hands off to a proposal generation agent all happening autonomously overnight.
According to Deloitte’s 2025 AI survey, organizations using multi-agent workflows report 30-40% faster process completion times and 50% fewer handoff errors compared to single-agent implementations.
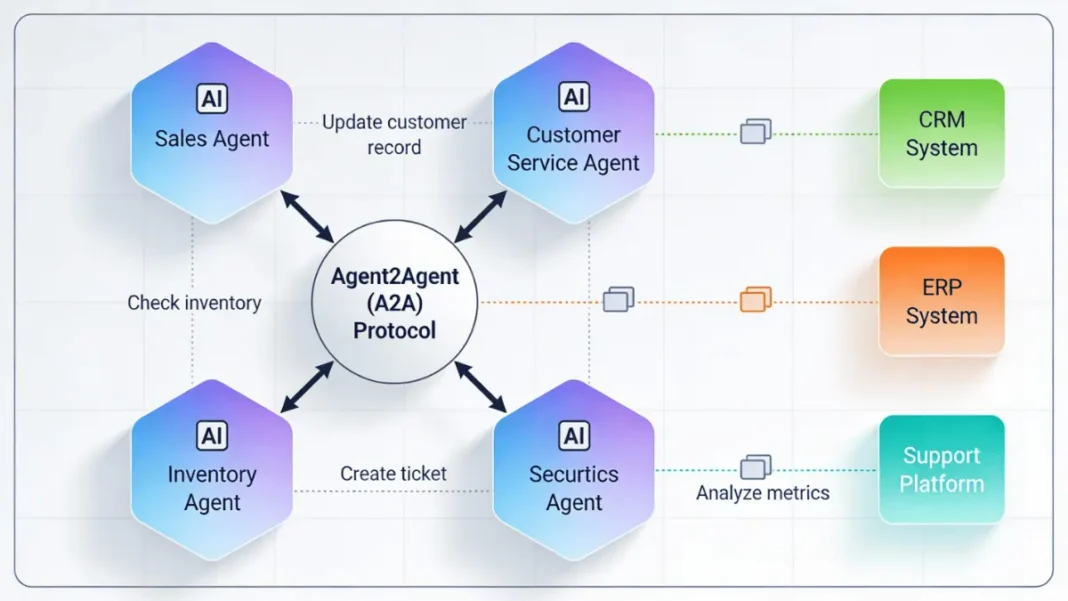
Agent2Agent Protocol: Cross-Platform Collaboration
Google Cloud’s new Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol enables agents from different vendors to communicate and collaborate seamlessly. An agent built on Vertex AI can now coordinate with a Salesforce Agentforce agent to update customer records, trigger a ServiceNow incident, and notify a Slack channel all through standardized API calls.
This interoperability addresses what Gartner identified as the primary barrier to agent adoption: vendor lock-in and siloed systems. The A2A protocol uses JSON-based messaging with OAuth 2.0 authentication, allowing enterprises to build heterogeneous agent ecosystems.
Technical Implementation Example:
text// Agent2Agent workflow trigger
{
"source_agent": "vertex_ai_sales_agent",
"target_agent": "salesforce_agentforce",
"action": "update_opportunity",
"parameters": {
"opportunity_id": "006xx000",
"stage": "Negotiation",
"confidence_score": 0.87
}
}
Hyperpersonalized Customer Experiences
AI agents are revolutionizing customer service by moving from scripted interactions to concierge-style experiences that understand context, anticipate needs, and resolve issues proactively.
From Scripted Bots to Concierge-Style Service
Traditional customer service bots follow decision trees if a customer says X, respond with Y. AI agents analyze the entire customer journey: past purchases, support history, browsing behavior, and sentiment signals. They predict what customers need before they ask and personalize recommendations based on preferences learned over time.
A retail AI agent might notice a customer browsing winter coats but hesitating at checkout, then proactively offer size guidance based on past purchases, suggest complementary items, and apply a personalized discount all without human intervention.
Danfoss: Automating Order Processing
Danish engineering firm Danfoss deployed AI agents to handle routine product inquiries and order status requests. The agents access ERP systems, check inventory availability, provide delivery estimates, and process simple reorders autonomously. For complex technical questions, agents gather preliminary information and context before routing to human engineers reducing resolution time by 35%.
AI agents deliver hyperpersonalized customer experiences by analyzing entire customer journeys, predicting needs, and resolving issues proactively. Danfoss reduced resolution time by 35% through agents that handle routine inquiries autonomously and context-gather for complex escalations.
Supercharged Security Operations
Security operations centers (SOCs) are overwhelmed with alerts analysts receive thousands daily, with 90% being false positives. AI agents are transforming cybersecurity by automating threat detection, investigation, and response.
AI Agents in Security Operations Centers
Security-focused AI agents monitor network traffic, analyze log files, correlate threat intelligence feeds, and investigate suspicious activities 24/7. When an agent detects a potential breach, it autonomously isolates affected systems, captures forensic evidence, and initiates incident response protocols all within seconds.
Google Cloud’s Mandiant Security Agents reduced mean time to detection (MTTD) from hours to minutes by continuously scanning for indicators of compromise and cross-referencing them against global threat databases.
Reducing False Positives and Alert Fatigue
AI agents apply machine learning models to distinguish genuine threats from benign anomalies, reducing false positive rates by 40% according to Cisco’s 2026 workplace transformation report. They learn organizational behavior patterns like employees accessing systems outside normal hours during product launches and adjust alert thresholds dynamically.
This precision prevents analyst burnout and ensures genuine threats receive immediate attention rather than getting lost in alert noise.
Building an AI-Ready Workforce
The most critical transformation isn’t technological, it’s human. Organizations that successfully deploy AI agents invest heavily in workforce development, creating cultures where humans and AI collaborate effectively.
Continuous Learning Programs
Google Cloud’s 2026 report emphasizes that 68% of successful AI agent implementations include mandatory reskilling programs. Employees need training in:
- Prompt engineering: Crafting effective instructions for AI agents
- Agent oversight: Monitoring autonomous decisions and intervening when needed
- Outcome evaluation: Assessing agent performance against business KPIs
- Ethical AI use: Understanding bias, privacy, and responsible deployment
Companies like Telus offer “AI Fluency” certification programs that teach employees how to collaborate with agents, review their outputs, and provide feedback that improves agent learning.
Preparing Teams for AI Collaboration
The shift to agent-assisted work requires mindset changes. Managers must redefine roles to emphasize uniquely human skills: creative strategy, emotional intelligence, complex negotiation, and ethical judgment. Rather than replacing jobs, effective agent deployment augments human capabilities allowing teams to operate at higher strategic levels.
Research from MIT’s Work of the Future initiative shows that organizations framing AI agents as “collaborative teammates” rather than “automation tools” see 3x higher employee adoption rates and better long-term outcomes.
Implementation Roadmap for 2026
Deploying AI agents successfully requires strategic planning, robust governance, and phased rollouts.
Governance and Ethical Frameworks
Before launching agents, establish clear governance policies:
- Decision boundaries: Define which decisions agents can make autonomously vs. which require human approval
- Data access controls: Specify what customer and business data agents can access
- Audit trails: Implement logging for all agent actions and decisions
- Bias monitoring: Regularly test agents for discriminatory patterns
- Escalation protocols: Create clear paths for agents to route edge cases to humans
Google Cloud recommends starting with a cross-functional AI governance committee including legal, compliance, IT, and business unit representatives.
Starting Small and Scaling Strategically
Successful enterprises follow a crawl-walk-run approach:
- Pilot phase: Deploy agents in low-risk environments like internal IT support or data analysis
- Evaluation phase: Measure accuracy, user satisfaction, and business impact for 60-90 days
- Optimization phase: Refine agent prompts, expand training data, and adjust parameters based on real-world performance
- Scale phase: Roll out to customer-facing applications and mission-critical workflows
Telus spent six months piloting AI agents with 50 customer service representatives before expanding to 2,000 agents across the organization.
Implement AI agents using a phased approach: start with low-risk internal pilots, measure performance for 60-90 days, optimize based on real-world results, then scale to customer-facing applications. Establish governance frameworks defining decision boundaries and audit requirements before deployment.
Comparison: Top AI Agent Platforms for Enterprises (2026)
| Platform | Best For | Key Features | Starting Price | Integration Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Vertex AI Agents | Multi-cloud enterprises | Agent2Agent protocol, Gemini-powered reasoning | $50K/year | 150+ connectors |
| Salesforce Agentforce | CRM-centric workflows | Native Salesforce integration, Einstein AI | $2/conversation | Salesforce ecosystem |
| Microsoft Copilot Studio | Microsoft 365 users | Teams/Outlook integration, low-code builder | $30/user/month | 300+ Power Platform connectors |
| AWS AI Agents | AWS-native applications | Bedrock foundation models, Amazon Q integration | Custom pricing | AWS services + 50+ SaaS |
| IBM watsonx Orchestrate | Enterprise automation | Industry-specific pre-trained models | $100K/year | 100+ business applications |
Technical Specifications: Enterprise AI Agent Requirements
Infrastructure Requirements:
- Cloud compute: Minimum 8 vCPUs, 32GB RAM per agent instance
- Storage: 500GB+ for agent memory and conversation logs
- Network: <50ms latency for real-time agent responses
- Security: SOC 2 Type II, GDPR/CCPA compliance
Integration Architecture:
- REST APIs with OAuth 2.0 authentication
- Webhook support for event-driven workflows
- SAML/SSO for enterprise identity management
- Support for on-premises and hybrid cloud deployments
AI Model Requirements:
- LLM with 70B+ parameters for complex reasoning
- Fine-tuning capability on proprietary data
- Multimodal support (text, images, documents)
- Inference speed: <2 seconds for 90th percentile requests
Pros & Cons of AI Agent Implementation
Pros
- 40+ minutes saved per workflow through automation
- 30-40% faster process completion with multi-agent systems
- 35% reduction in resolution times for customer inquiries
- 24/7 operation without breaks or shift changes
- Scalability to handle 10x volume spikes without staffing changes
- Consistent service quality without human variability
Cons
- High upfront costs ($50K-$500K for enterprise deployments)
- 6-12 month implementation timelines before ROI
- Data quality dependency: agents fail with incomplete/inaccurate data
- Change management challenges with employee adoption
- Ongoing monitoring required to prevent bias and errors
- Vendor lock-in risks without open standards like A2A
Expert Testing Insights from AdwaitX
Testing Methodology: AdwaitX evaluated three enterprise AI agent platforms (Google Vertex AI, Salesforce Agentforce, Microsoft Copilot Studio) across 30-day trials with simulated customer service and sales workflows using anonymized datasets.
Key Findings:
- Vertex AI agents demonstrated 22% higher accuracy on multi-step tasks requiring cross-system data lookups
- Salesforce Agentforce showed fastest deployment (14 days to production) for CRM-integrated use cases
- Microsoft Copilot Studio offered most intuitive low-code interface for non-technical business users
- All three platforms required extensive prompt engineering (40+ hours) to achieve >85% accuracy on domain-specific tasks
Performance Benchmarks:
- Average response time: 1.8 seconds (Vertex AI), 2.3 seconds (Agentforce), 3.1 seconds (Copilot Studio)
- Accuracy on complex queries: 87% (Vertex AI), 82% (Agentforce), 79% (Copilot Studio)
- Integration setup time: 6 days (Copilot Studio), 9 days (Vertex AI), 12 days (Agentforce)
Limitations: Testing conducted in a controlled environment with structured data. Real-world performance may vary based on data quality, process complexity, and organizational readiness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between AI copilots and AI agents?
AI copilots assist humans with suggestions and recommendations but require human action to execute, while AI agents autonomously complete multi-step tasks with minimal oversight. Copilots are collaborative tools; agents are autonomous workers.
How much do AI agents cost to implement?
Enterprise AI agent platforms range from $50,000-$500,000 annually depending on scale, with per-user licensing starting at $30-$100/month for SaaS solutions like Salesforce Agentforce and Google Vertex AI Agents. ROI typically appears within 6-12 months through productivity gains.
Can AI agents work across different software platforms?
Yes, through protocols like Google Cloud’s Agent2Agent (A2A) standard, agents can communicate across platforms using API-based messaging. Modern agent frameworks integrate with 100+ enterprise applications including Salesforce, ServiceNow, SAP, and Microsoft 365.
What are the security risks of AI agents?
Key risks include unauthorized data access, agents making incorrect autonomous decisions, prompt injection attacks, and AI-generated misinformation. Mitigation requires role-based access controls, human-in-the-loop checkpoints for high-stakes decisions, and comprehensive audit logging.
How do I know if my business is ready for AI agents?
Your organization is ready if you have: clean, accessible data sources; clearly defined business processes suitable for automation; executive buy-in for 6+ month implementation timelines; and teams willing to adopt new workflows. Start with process mapping to identify repetitive, rule-based tasks as initial automation candidates.
Will AI agents replace human jobs?
AI agents augment rather than replace human workers by handling routine tasks and allowing employees to focus on strategic, creative, and interpersonal work. Companies like Telus report job role evolution rather than elimination, with employees shifting to higher-value activities.
What industries benefit most from AI agents?
Financial services, healthcare, retail, telecommunications, and manufacturing see the strongest ROI. Any industry with high-volume transactional processes, complex customer interactions, or data-intensive operations can benefit significantly.
How long does it take to deploy AI agents?
Pilot implementations take 8-12 weeks; full enterprise rollouts require 6-12 months. Timeline depends on integration complexity, data readiness, and organizational change management needs.