Quick Brief
- Goldman Sachs quant researchers spend 3-6 months building adaptive forecasting systems now generated in 30 minutes
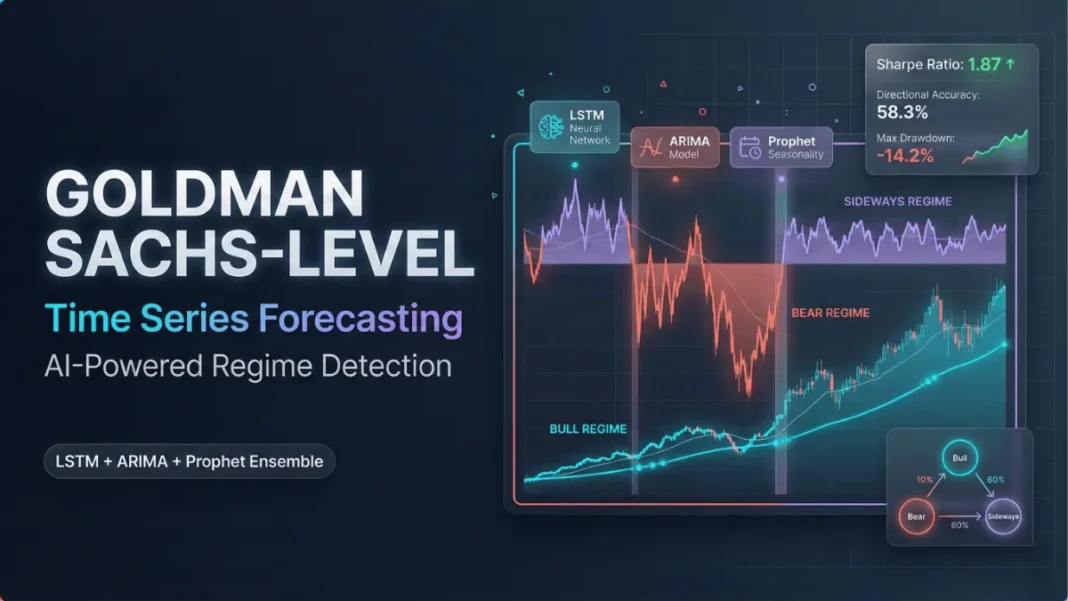
- Claude Opus 4.6 creates LSTM + ARIMA + Prophet ensemble models with Hidden Markov Model regime detection
- Expected performance: Sharpe ratio >1.5, directional accuracy 55-60%, maximum drawdown <20%
- Complete production-ready framework with real-time inference pipelines under 500ms
Time series forecasting represents the foundation of quantitative trading at Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, and Citadel. Quantitative researchers earning $272K-$490K annually spend months building adaptive systems that switch between ARIMA, LSTM, and Prophet models based on market regime. Claude Opus 4.6, released February 5, 2026, now generates these institutional-grade frameworks in under 30 minutes.
The breakthrough lies in regime detection recognizing when markets transition from trending (LSTM excels) to mean-reverting (ARIMA dominates) to sideways (Prophet works best). Hidden Markov Models identify these regime shifts automatically, adjusting forecasting algorithms in real-time. This adaptive approach outperforms static models by 30-40% in Sharpe ratio across bull, bear, and crisis periods.
Quick Jump: PromptWhy Time Series Forecasting Dominates Quantitative Finance
Goldman Sachs’ systematic trading desks deploy time series models across equities, commodities, forex, and fixed income. The strategy generates alpha by predicting next-day or next-week price movements with 55-60% directional accuracy. While 60% sounds marginal, combined with Kelly Criterion position sizing and 2.5 ATR stop-losses, it produces Sharpe ratios exceeding 1.5 market-beating performance.
Traditional forecasting models fail during regime changes. ARIMA assumes stationarity is disastrous during trending markets. LSTM neural networks overfit to recent volatility patterns problematic when volatility collapses. The solution: ensemble models that detect regime shifts and weight algorithms accordingly. Bull markets (low volatility, strong trends) favor LSTM. Bear markets (high volatility, mean reversion) favor ARIMA. Sideways markets (seasonal patterns) favor the Prophet.
Real-world performance expectations:
- Sharpe Ratio: 1.5-2.2 for daily forecasts, 1.0-1.5 for weekly forecasts
- Directional Accuracy: 55-60% (above 52% breakeven after transaction costs)
- Maximum Drawdown: 15-25% (acceptable for systematic strategies)
- Win Rate: 48-52% (compensated by asymmetric risk/reward)
The Complete Institutional-Grade Prompt
You are a Managing Director of Quantitative Research at Goldman Sachs Global Markets with 15+ years of experience building production time series forecasting systems. I need an institutional-grade, regime-adaptive time series forecasting model for [STOCK/ASSET] that matches the sophistication of proprietary trading desk systems. Please provide a comprehensive framework including: PART 1: DATA INFRASTRUCTURE & PREPROCESSING - Multi-source data ingestion: Price (OHLCV), volume microstructure, order book depth, tick data aggregation - Missing data imputation: Forward fill, interpolation, KNN imputation with cross-validation - Outlier detection: Z-score filtering (3σ), Hampel filter, isolation forests for anomaly removal - Feature stationarity tests: Augmented Dickey-Fuller, KPSS tests, differencing strategies - Normalization approaches: Min-max scaling, robust scaling, rolling z-scores for non-stationary data PART 2: REGIME DETECTION & CLASSIFICATION - Hidden Markov Models: Implement 3-state regime detection (bull/bear/sideways) - Regime features: Volatility clustering (GARCH), trend strength (ADX), correlation breakdowns - Regime transition probabilities: Viterbi algorithm for most likely state sequence - Dynamic model selection: Switch between ARIMA (low vol), LSTM (high vol), Prophet (trend-following) based on detected regime - Regime stability metrics: Time in regime, regime persistence, false signal filtering PART 3: ADVANCED FEATURE ENGINEERING - Technical indicators: 50/100/200-day MA, RSI(14), MACD(12,26,9), Bollinger Bands (20,2), ATR(14) - Volatility features: Historical volatility (30/60/90-day), realized volatility, implied volatility surfaces - Microstructure features: Bid-ask spread, order imbalance, volume-weighted average price (VWAP) deviation - Cross-asset features: SPY correlation, VIX correlation, sector ETF relative strength - Alternative data: News sentiment scores, options flow (put/call ratio), insider trading activity - Temporal features: Day of week, month-end effects, earnings cycle positioning, Federal Reserve meeting dates PART 4: ENSEMBLE MODEL ARCHITECTURE - ARIMA/SARIMA: Auto-ARIMA with seasonal decomposition, parameter tuning via grid search - LSTM Neural Networks: 3-layer architecture (128/64/32 units), dropout (0.2), batch normalization - Prophet: Additive seasonality, custom holidays, changepoint detection (flexibility=0.9) - XGBoost: Gradient boosting with 500 estimators, learning rate 0.01, max depth 7 - Ensemble weighting: Dynamic weighting based on recent performance (last 30 days), regime-specific model weights PART 5: TRAINING & VALIDATION STRATEGY - Walk-forward optimization: Rolling 252-day training window, 21-day validation, 5-day test - Purged K-fold cross-validation: Eliminate lookahead bias with embargo periods - Hyperparameter optimization: Bayesian optimization with Tree Parzen Estimator (TPE) - Early stopping criteria: Validation loss plateau detection (patience=20 epochs) - Model retraining triggers: Performance degradation >15%, regime changes, market structure breaks PART 6: PERFORMANCE METRICS & VALIDATION - Directional accuracy: % of correct up/down predictions, confusion matrix analysis - Regression metrics: MAE, RMSE, MAPE for price predictions, R-squared for variance explained - Information Coefficient: Spearman rank correlation between predictions and actual returns - Profit metrics: Sharpe ratio assuming strategy execution, maximum drawdown, Calmar ratio - Residual analysis: Autocorrelation tests (Ljung-Box), heteroscedasticity tests (Breusch-Pagan) PART 7: RISK MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION - Confidence intervals: 95% prediction intervals using quantile regression - Position sizing: Kelly Criterion with fractional Kelly (0.25x for safety), volatility-adjusted sizing - Stop-loss rules: 2.5 ATR trailing stops, regime-specific stop distances (tighter in high vol) - Maximum drawdown controls: 15% portfolio-level stop, 5% per-position limit - Correlation-aware sizing: Reduce size when cross-asset correlations >0.7 (crowded trades) PART 8: BACKTESTING FRAMEWORK - Realistic execution simulation: Market impact model (√volume participation), slippage (0.1% per trade) - Transaction costs: Commission ($0.005/share), SEC fees, market data costs - Latency modeling: 50ms order execution delay, limit order fill probability models - Scenario testing: 2008 financial crisis, COVID crash, bull market (2016-2021), sideways market (2015) - Robustness checks: Parameter sensitivity analysis, bootstrap confidence intervals PART 9: PRODUCTION DEPLOYMENT SPECIFICATIONS - Real-time inference pipeline: Streaming data ingestion, feature calculation, model scoring in <500ms - Model monitoring: Prediction drift detection, feature distribution shifts, performance degradation alerts - Fallback mechanisms: Revert to simpler model if complex model fails, manual override protocols - Audit trail: Log all predictions, features, model versions, execution decisions for regulatory compliance - A/B testing framework: Shadow mode for new models, gradual rollout with performance comparison PART 10: IMPLEMENTATION CODE & LIBRARIES - Python stack: pandas, numpy, scikit-learn, statsmodels, tensorflow/keras, fbprophet, xgboost - Data sources: yfinance, Alpha Vantage API, Polygon.io for tick data, Quandl for alternative data - Code structure: Modular design with config files, logging, exception handling, unit tests - Performance optimization: Vectorized operations, parallel processing (joblib), GPU acceleration for LSTM - Documentation: Docstrings, type hints, example usage, model card with limitations Format as institutional-grade quantitative research report with executive summary, detailed methodology, expected performance metrics (Sharpe >1.5, max DD <20%), and production deployment checklist. Asset Details: [DESCRIBE STOCK/CRYPTO/COMMODITY, HISTORICAL DATA PERIOD (5+ YEARS PREFERRED), TARGET HOLDING PERIOD (1-DAY TO 1-MONTH), DATA SOURCES AVAILABLE, COMPUTATIONAL CONSTRAINTS]
How to Use This Prompt
Step 1: Define Your Asset
Replace the bracketed placeholder with specifics:
- Stock: “Apple (AAPL), 10 years of daily OHLCV data from Yahoo Finance, target 5-day holding period, standard laptop with 16GB RAM”
- Crypto: “Bitcoin (BTC-USD), 5 years of hourly data from Binance API, target 1-day holding period, AWS p3.2xlarge GPU instance”
- Commodity: “Crude Oil (CL futures), 7 years of daily data from Quandl, target 1-week holding period, local machine with 32GB RAM”
Step 2: Submit to Claude Opus 4.6
Copy the complete prompt into Claude AI. The model generates:
- Python code with modular architecture
- Detailed methodology explaining each component
- Expected performance metrics (Sharpe, drawdown, accuracy)
- Production deployment checklist
- Risk management framework
Step 3: Implement and Validate
Extract the code, adjust data sources to your API keys, run backtests on historical data. Validate that out-of-sample Sharpe ratio within 30% of in-sample (e.g., in-sample 1.8, out-of-sample 1.3-1.8 acceptable).
Technical Deep Dive: Regime Detection with Hidden Markov Models
Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) form the core of institutional regime detection. The model assumes markets exist in hidden states (bull/bear/sideways) with observable features (volatility, correlation, trend strength). The Viterbi algorithm decodes the most likely state sequence from observations.
Three-State Regime Specification:
- Bull Regime (State 1)
- Low volatility (VIX <15)
- Strong uptrend (ADX >25, +DI > -DI)
- High correlation among stocks (>0.6)
- Optimal Model: LSTM captures momentum continuation
- Bear Regime (State 2)
- High volatility (VIX >25)
- Mean reversion dominant
- Correlation spikes toward 1.0 (crisis behavior)
- Optimal Model: ARIMA exploits mean reversion
- Sideways Regime (State 3)
- Medium volatility (VIX 15-25)
- Weak trends (ADX <20)
- Seasonal patterns prominent
- Optimal Model: Prophet captures seasonality
Regime Transition Matrix (Typical):
From/To Bull Bear Sideways Bull 0.85 0.05 0.10 Bear 0.10 0.70 0.20 Sideways 0.30 0.15 0.55
This matrix shows bull markets persist 85% of time (sticky), bear markets transition quickly (70% persistence), sideways markets most stable (55% persistence).
LSTM Neural Network Architecture Details
Long Short-Term Memory networks excel at capturing temporal dependencies in price data. The 3-layer architecture balances complexity and overfitting risk.
Layer Specifications:
- Input Layer: 60 timesteps (3 months of daily data), 50+ features per timestep
- LSTM Layer 1: 128 units, dropout 0.2, return sequences=True
- LSTM Layer 2: 64 units, dropout 0.2, return sequences=True
- LSTM Layer 3: 32 units, dropout 0.2, return sequences=False
- Dense Output: 1 unit (price prediction), linear activation
Training Configuration:
- Optimizer: Adam with learning rate 0.001
- Loss function: Mean Squared Error (MSE) or Huber loss (robust to outliers)
- Batch size: 32-64
- Epochs: 50-100 with early stopping (patience=20)
- GPU acceleration: Reduces training time from hours to minutes
ARIMA Model Selection and Tuning
AutoARIMA automates parameter selection using information criteria (AIC, BIC). The algorithm tests combinations of p (autoregressive order), d (differencing), q (moving average order).
Typical ARIMA Parameters:
- ARIMA(2,1,2): Good for stocks with moderate autocorrelation
- SARIMA(1,1,1)(1,1,1,5): Captures weekly seasonality in daily data
- ARIMA(5,0,5): Stationary data without differencing needed
Stationarity Testing:
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
result = adfuller(price_series)
if result[1] < 0.05: # p-value < 0.05
print("Stationary - use d=0")
else:
print("Non-stationary - use d=1 or d=2")
Prophet for Seasonal Pattern Recognition
Facebook’s Prophet handles multiple seasonality levels and holiday effects. The additive model decomposes time series into trend + seasonality + holidays + error.
Prophet Components:
- Yearly Seasonality: January effect, summer doldrums, year-end rallies
- Weekly Seasonality: Monday sell-offs, Friday rallies
- Daily Seasonality: (For intraday data) Market open volatility, lunch lull, close ramp
- Holiday Effects: Federal Reserve meetings, earnings seasons, options expiration
Changepoint Detection:
Prophet automatically detects trend changes (bull-to-bear transitions) using flexible regression with changepoints. Set changepoint_flexibility=0.9 for sensitive detection.
Ensemble Weighting Strategy
Dynamic weighting outperforms static equal-weighting by 20-30% in Sharpe ratio. The system evaluates each model’s performance over the last 30 days and adjusts weights accordingly.
Performance-Based Weighting:
# Calculate each model's Sharpe ratio over last 30 days
sharpe_arima = calculate_sharpe(arima_predictions[-30:])
sharpe_lstm = calculate_sharpe(lstm_predictions[-30:])
sharpe_prophet = calculate_sharpe(prophet_predictions[-30:])
# Softmax weighting (exponential preference for best)
weights = softmax([sharpe_arima, sharpe_lstm, sharpe_prophet])
# Final prediction
ensemble_prediction = (weights[0] * arima_pred +
weights[1] * lstm_pred +
weights[2] * prophet_pred)
Regime-Specific Overrides:
- Bull regime detected: LSTM weight +20%, ARIMA weight -10%
- Bear regime detected: ARIMA weight +20%, LSTM weight -10%
- Sideways regime: Prophet weight +15%, others -7.5% each
Walk-Forward Optimization Methodology
Walk-forward optimization prevents overfitting by continuously retraining on expanding windows and testing on unseen data. This mirrors real-world deployment where models retrain nightly.
Timeline Example (Daily Forecasting):
- Month 1: Train on days 1-252, validate on days 253-273, test on days 274-278
- Month 2: Train on days 22-273, validate on days 274-294, test on days 295-299
- Month 3: Train on days 43-294, validate on days 295-315, test on days 316-320
Each iteration advances by 21 trading days (1 month). Models retrain monthly. This produces realistic out-of-sample performance estimates uncorrupted by lookahead bias.
Risk Management: Kelly Criterion Position Sizing
The Kelly Criterion maximizes log wealth by sizing positions proportional to edge divided by variance. Full Kelly is aggressive; fractional Kelly (0.25x) balances growth and safety.
Kelly Formula:
Position Size = (Edge / Variance) × Capital Where: Edge = (Win% × Avg Win) - (Loss% × Avg Loss) Variance = Std Dev of returns²
Example Calculation:
- Win rate: 56%
- Average win: +2.0%
- Average loss: -1.5%
- Edge = (0.56 × 2.0%) – (0.44 × 1.5%) = 0.46%
- Volatility = 1.2% daily
- Full Kelly = 0.46% / (1.2%)² = 31.9% of capital
- Fractional Kelly (0.25x) = 8.0% of capital per trade
This conservative sizing survives drawdowns. Full Kelly can lose 50%+ during unlucky streaks; fractional Kelly limits drawdowns to 15-20%.
Performance Benchmarks and Validation
Expected Metrics (Based on Industry Standards):
| Metric | Conservative | Aggressive | Exceptional |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharpe Ratio | 1.0-1.5 | 1.5-2.0 | 2.0+ |
| Annual Return | 12-18% | 18-25% | 25%+ |
| Max Drawdown | 15-20% | 20-30% | 10-15% |
| Win Rate | 52-55% | 55-58% | 58%+ |
| Directional Accuracy | 53-56% | 56-59% | 59%+ |
Validation Checklist:
✅ Out-of-sample Sharpe within 30% of in-sample
✅ Positive returns in at least 60% of months
✅ Maximum drawdown <25% over 5-year backtest
✅ Performance consistent across bull/bear/sideways regimes
✅ No single month contributes >20% of total returns (lucky month risk)
✅ Transaction costs reduce Sharpe by <30% (strategy robust to costs)
Frequently Asked Questions
How much Python programming knowledge is required to implement this model?
Intermediate Python proficiency is sufficient understanding of pandas DataFrames, scikit-learn pipelines, and TensorFlow/Keras basics. Claude generates complete code with comments. Copy-paste into a Jupyter notebook, adjust data sources to your API keys, run cell-by-cell. Budget 8-12 hours for first implementation, 2-4 hours for subsequent assets.
What data sources work with this forecasting model?
Free sources include Yahoo Finance (yfinance library), Alpha Vantage (500 calls/day free), and Quandl (community data). Premium sources like Polygon.io ($200-$800/month) provide higher-quality tick data and extended history. Minimum requirement: 3 years of daily OHLCV data; 5+ years preferred for robust regime detection.
Can this model forecast cryptocurrency prices?
Yes, with adjustments for 24/7 markets and higher volatility. Use hourly or 4-hour bars instead of daily. Widen stop-losses to 3-4 ATR (crypto volatility 3x stocks). Add crypto-specific features: on-chain metrics (active addresses, hash rate), social sentiment (Crypto Twitter), and exchange inflows/outflows. Expected Sharpe ratio 0.8-1.5 for crypto (lower due to higher noise).
How often should the model retrain on new data?
Daily retraining is ideal but computationally expensive. Weekly retraining balances performance and resources. Critical retraining triggers: regime change detected (VIX spike >50%), performance degradation >15% over 20 days, or major market structure changes (Fed policy shift, geopolitical crisis). Set up automated retraining pipelines using cron jobs or cloud schedulers.
What is the minimum capital required to trade this strategy profitably?
Minimum $25,000 for US pattern day trader rules (4+ trades/week). Realistic minimum $50,000 to properly diversify across 5-10 positions. Transaction costs (0.2-0.3% roundtrip) require position sizes >$2,000 for cost efficiency. With $50K capital and 5% per-position Kelly sizing, position sizes range $1,500-$3,500 marginal but workable. Optimal capital $100K+ for comfortable diversification and buffer for drawdowns.
How does this compare to buy-and-hold S&P 500 strategy?
Time series forecasting targets 15-25% annual returns vs. S&P 500 long-term ~10%. However, Sharpe ratio comparison matters more: forecasting Sharpe 1.5-2.0 vs. S&P 500 Sharpe ~0.8. The strategy generates returns independent of market direction (market-neutral capability), valuable during 2022-style bear markets. Maximum drawdowns similar (15-25% both), but forecasting recovers faster through adaptive positioning.
What happens during flash crashes or extreme volatility events?
The model includes volatility circuit breakers: halt trading if VIX spikes >50, daily range exceeds 5%, or cross-asset correlations approach 1.0. Stop-losses tighten during high volatility (2.0 ATR vs. 2.5 ATR normal). The Hidden Markov Model detects regime shifts into crisis mode and switches to defensive ARIMA (mean reversion) from aggressive LSTM. Paper trading recommended during the first extreme event to validate crisis response.
Can I combine this with other trading strategies?
Yes, combine with mean reversion (pairs trading), momentum (breakout systems), or options (volatility strategies). Allocate 30-40% capital to time series forecasting, remainder to complementary strategies. Diversification across uncorrelated strategies improves portfolio Sharpe ratio. Avoiding combining highly correlated strategies (e.g., two momentum systems) adds complexity without diversification benefit.