Apple’s Foundation Models framework lets developers build private, on-device AI features that run fast, work offline, and don’t rack up inference bills. It taps a compact ~3B model that supports guided generation and tool calling, with tight Swift integration. Early apps show clear wins in workouts, journaling, education, and productivity.
Table of Contents
What is Apple’s Foundation Models framework?
Apple’s Foundation Models framework is a developer layer that exposes the same on-device language model powering Apple Intelligence. The headline benefits are privacy, offline availability, and zero per-token or per-call inference fees. It’s meant for app features that need quick, typed, and reliable responses without shipping data to a server.
The 3B on-device model at the core of Apple Intelligence
Under the hood is a ~3-billion-parameter model tuned for text understanding, transformation, summarization, short dialog, and structured output. It’s optimized for Apple silicon so it starts fast, keeps latency low, and sips power compared with large cloud models. Apple also supports a server-side family for heavier tasks, but the framework’s default path is the local model.
Why “free inference” matters
Normally, every AI call has a cost, which nudges teams to rate-limit features or lock them behind paywalls. Apple’s on-device path removes that line item. You still pay the one-time cost of development and QA, but not per-use inference bills. For features that run dozens of times a day—title suggestions, summaries, tags—this can be the difference between “fun demo” and “shipped to everyone.”
Privacy and offline support
Because the model runs locally, sensitive text doesn’t need to leave the device. For use-cases like health notes, contracts, or student work, that’s a big trust win. Offline also means your feature works on a plane or in a dead zone. If your app already caches the right context, the model can still act.
How the framework works (in practice)
Guided generation: predictable, typed outputs
LLMs often return free-form text you have to parse. Guided generation flips that dynamic. You describe the structure you want (think: a Swift struct for WorkoutPlan with fields for name, sets, reps, rest). The model then returns output that fits that mold. It stays within your schema, so your UI can render with fewer checks and brittle parsers. In short: less glue code, fewer edge-case crashes.
Tool calling: bring your app’s knowledge into the loop
Tool calling lets the model ask your app for facts it doesn’t know. That could be a user’s workout history, a glossary entry, or pricing from your local store cache. You expose a set of tools, the model learns when to call them, and your feature feels “aware” without sending data to a cloud LLM. It’s especially useful for precise answers and grounding.
Swift integration: minimal code to first result
Apple wired this into Swift so you can move quickly. You define the output types, prompt with your input, and get back typed data. For teams already deep in SwiftUI, it’s a low-friction add: fetch, render, test. That short path matters when you’re iterating on prompts and UX.
Performance notes
On-device inference is designed for responsiveness. For longer tasks or heavy context windows, you may still want a server fallback. A hybrid design works well: keep privacy-sensitive or quick interactions local; send large, research-style jobs to your own endpoint or a partner when users opt in.
Real-world examples you can learn from
Early adopters give a good sense of what to build:
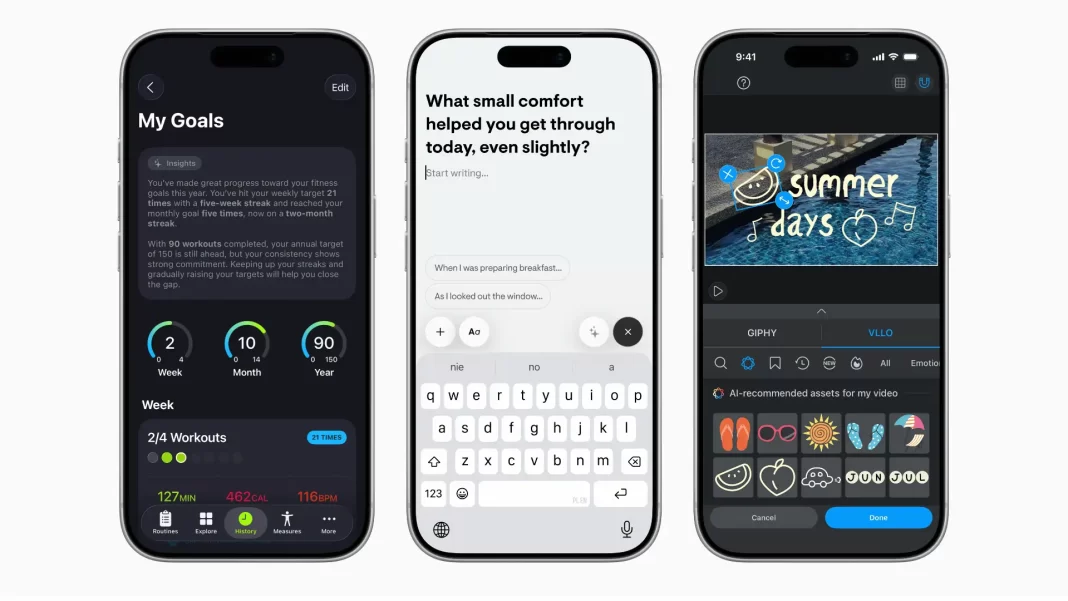
Health & fitness. SmartGym turns a plain-English workout description into a structured routine with sets, reps, rest times, and equipment adjustments. It now explains the “why” behind suggested tweaks. 7 Minute Workout lets users add constraints like “avoid knee strain” or “training for a 5K.” Train Fitness can swap exercises when the right equipment isn’t available. These are small, useful touches that meet people where they are.
Journaling & wellbeing. Stoic generates prompts that adapt to your recent entries and mood. Gratitude creates weekly summaries of wins and challenges, then suggests affirmations pulled from your own words. These features feel personal without sending private text to a server.
Education. CellWalk mixes interactive 3D biology with conversational explanations of terms. The model grounds its answers with the app’s own science content so explanations stay accurate. Apps like Grammo and Vocabulary create exercises on the fly and auto-organize words into themes. Platzi answers questions about the exact video lesson you’re watching.
Productivity & creation. Stuff understands dates, tags, and lists as you type. Speak a few reminders and it turns them into tasks. Signeasy summarizes contracts and highlights key points. Agenda’s “Ask Agenda” pulls answers from your personal notes. Detail turns a draft into a ready-to-read teleprompter script, and can generate titles, descriptions, and tags for sharing. OmniFocus helps you turn a vague plan (“3-day trip to Jaipur”) into a project with next actions. VLLO analyzes scenes to suggest music and stickers, blending the Foundation Models framework with Vision features.
If you squint, a pattern shows up: the best wins are small, context-aware boosts that save a minute here and five minutes there. The model isn’t trying to be a chat app. It’s quietly improving the task people opened your app for.
Devices and availability
Supported devices. Apple Intelligence runs on a set of recent iPhone, iPad, and Mac devices with newer A-series and all M-series chips. If your users bought a flagship in the last couple of generations or use any M-series Mac they likely have access.
OS versions. The framework arrives with iOS 26, iPadOS 26, and macOS 26. Users get features once Apple Intelligence is enabled on their device. Rollouts vary by region and language, so build graceful fallbacks.
Feature caveats. Local models excel at short form understanding and transformation. For long documents or open-domain research, plan a hybrid approach and clear prompts that set expectations.
When to use on-device vs server (and when to mix)
On-device is best when:
- The input is sensitive (health notes, contracts, payments).
- Latency matters (typing assistant, live tagging, quick summaries).
- Usage is frequent and you want zero per-use cost.
Server is better when:
- You need broad world knowledge or very long context.
- You’re generating long-form content or complex code.
- You want to standardize responses across devices.
A simple rubric: default to local for anything short, private, and repeated; escalate to server for long, public, or rare tasks. Many teams ship both with a toggle or an “enhanced mode.”
Build checklist for your first feature
- Pick a job, not a demo. “Help users tag receipts as they type” beats “add AI somewhere.”
- Define your schema. Sketch the output struct early; guided generation thrives on clear types.
- Ground with tools. Create tools for facts you already store safely on device.
- Set guardrails. Show disclaimers for summaries; add a quick “Was this helpful?” prompt.
- Measure real outcomes. Track time saved, completion rate, and user edits.
- Design fallbacks. If Apple Intelligence is off or unavailable, keep core flows intact.
- Test battery and heat. Run worst-case scenarios on older supported hardware.
- Plan a hybrid. Offer an opt-in server path for heavy tasks with clear privacy notes.
Pros and cons at a glance
| On-device with Foundation Models | What you gain | What to watch |
|---|---|---|
| Private by default | Trust, compliance wins | Limited world knowledge |
| Offline capable | Works anywhere | Shorter context windows |
| No per-use fees | Scale to everyone | Hybrid path for long tasks |
| Swift-native types | Faster iteration | Careful UX for errors |
The Bottom Line
The Foundation Models framework is a practical way to add intelligence where it helps most: small, reliable boosts that feel native and respectful of user data. Start with one job your app already does, make it faster or clearer, measure the lift, and expand from there. That’s how teams are shipping wins today.
Frequently Asked Question
Does this work offline?
Yes. The framework is designed to run on-device. Many features work without a connection once you have the needed local context.
Is there an inference cost?
No usage-based fees for on-device calls. You avoid the per-token bills typical of cloud APIs.
How powerful is the on-device model?
It’s a compact ~3B model tuned for text-focused tasks like summarizing, extracting fields, rewriting, and short dialog. It’s not aiming to replace large general-knowledge chatbots.
What about privacy?
Inputs processed locally don’t leave the device. If you add an optional server path, disclose it clearly and get consent.
Which devices are supported?
Recent iPhones with newer A-series chips and all M-series iPad/Mac models support Apple Intelligence. Check Apple’s device list and plan fallbacks.
Can I fine-tune it?
Apple supports adapters for advanced use-cases. Start with the base model, ship value, then consider adapters if you truly need new skills.
Featured Answer Boxes
What is Apple’s Foundation Models framework?
It’s a developer layer that exposes Apple’s on-device language model to third-party apps. You get typed outputs via guided generation, grounding via tool calling, and private, offline inference with no usage fees. It’s built into iOS 26, iPadOS 26, and macOS 26.
Does it work offline and protect privacy?
Yes. The default path runs entirely on the device, so sensitive text doesn’t leave user hardware. Features keep working without connectivity as long as the needed context is stored locally. Hybrid server paths are optional and should be disclosed.
How strong is the model?
The core is a compact ~3B parameter model tuned for text understanding, extraction, summarization, and short dialog. It’s optimized for Apple silicon. For heavier tasks, Apple also operates server-side models; third-party apps can choose to combine approaches.
Why does “free inference” matter?
You don’t pay per-call fees for on-device usage. That makes everyday features summaries, tags, titles affordable to ship for all users, instead of gating them behind subscriptions or hard limits.
What are guided generation and tool calling?
Guided generation returns outputs that match your Swift types, so parsing is simpler and safer. Tool calling lets the model request specific info from your app (like history or local indexes), which keeps answers grounded and useful.