Quick Brief
- Codex app introduces multi-agent parallel workflows for macOS developers starting February 2, 2026
- Built-in Skills system extends capabilities beyond code to design implementation and cloud deployment
- Automations run scheduled tasks in background with review queue for continuous development
- Free and Go users get limited-time access while paid plans receive doubled rate limits
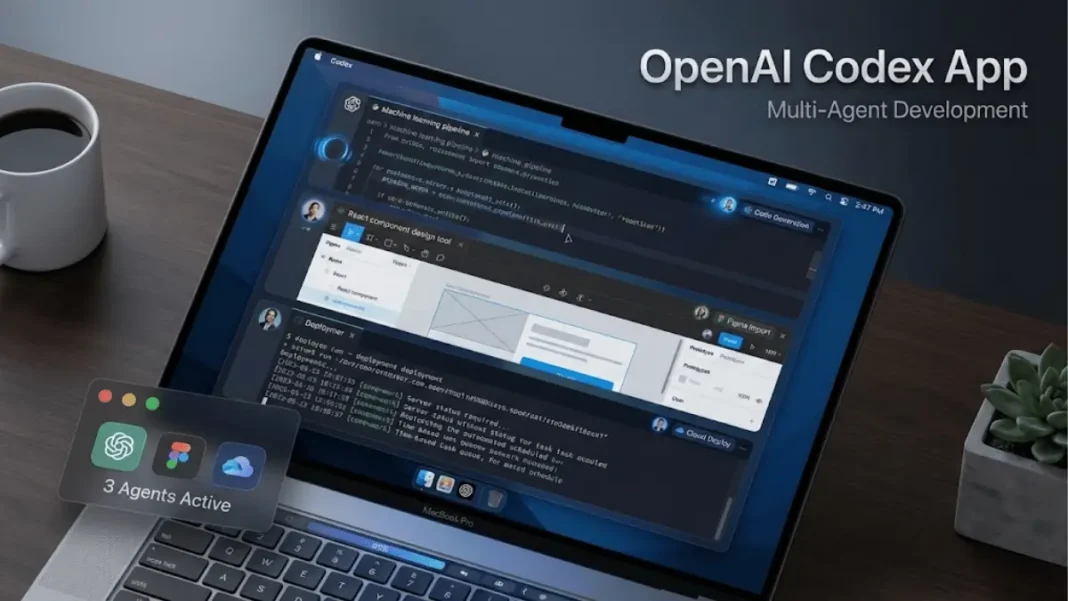
OpenAI just dismantled the traditional coding workflow and the Codex app proves it. Launched February 2, 2026, this macOS application transforms how developers supervise AI agents across long-running projects that span hours or weeks. You gain a command center for orchestrating multiple coding agents simultaneously, each working in isolated threads without conflicting with your local environment. This analysis reveals eight capabilities that separate Codex from conventional IDE tools and positions it as OpenAI’s direct response to Anthropic’s Claude Code.
Multi-Agent Workflows Replace Single-Task Coding
The Codex app organizes agents in separate threads by project, allowing seamless task-switching without context loss. Each agent operates on an isolated code copy through built-in worktree support, enabling exploration of different implementation paths without impacting your main codebase. You review agent changes within threads, comment on diffs, and open them in your preferred editor for manual adjustments.
The application synchronizes with existing Codex CLI and IDE extension configurations automatically. Your session history transfers immediately, eliminating setup friction when adopting the desktop interface. This integration allows switching between terminal, IDE, and app environments while maintaining continuous project state.
What is the Codex app’s primary advantage over traditional IDEs?
The Codex app provides dedicated multi-agent management that traditional IDEs lack. Agents run in parallel threads with worktree isolation, allowing simultaneous exploration of different code paths. You supervise multiple long-running tasks without terminal or IDE limitations.
Skills System Extends Beyond Code Generation
Skills bundle instructions, resources, and scripts that enable Codex to connect tools, execute workflows, and complete tasks matching team preferences. The app includes a dedicated interface for creating and managing these reusable capabilities. You explicitly request specific skills or allow automatic selection based on task requirements.
OpenAI demonstrated this with a racing game built using 7 million tokens from one initial prompt. Codex employed an image generation skill powered by GPT Image and a web game development skill to autonomously design, code, and QA test the complete application. The agent assumed designer, developer, and tester roles without additional human intervention.
The open-source skills library includes capabilities for Figma design implementation, Linear project management, cloud deployment to Cloudflare/Netlify/Render/Vercel, image generation, OpenAI API documentation access, and PDF/spreadsheet/docx creation. Teams share custom skills by checking them into repositories, making them available across CLI, IDE, and app environments.
Automations Handle Repetitive Development Tasks
Automations combine instructions with optional skills on user-defined schedules. Results land in a review queue upon completion, allowing you to continue work when needed. This background execution persists independent of active app sessions.
OpenAI teams use Automations for daily issue triage, CI failure summarization, release brief generation, and bug detection. These scheduled agents handle important but repetitive work that traditionally consumed developer time. The automation framework supports continuous monitoring without manual trigger requirements.
How do Codex Automations differ from traditional CI/CD pipelines?
Automations operate on natural language instructions with AI reasoning rather than rigid scripts. They combine multiple skills, adapt to changing conditions, and surface results in a review queue. Traditional CI/CD executes predefined commands without contextual understanding or adaptive problem-solving.
Security Architecture Balances Power with Control
The Codex app implements native open-source sandboxing at the system level. By default, agents limit file editing to the current folder or branch and use cached web search. Commands requiring elevated permissions like network access prompt for user approval.
Teams configure rule sets that allow specific commands to run with elevated permissions automatically. This project-level or team-level configuration provides flexibility without compromising security defaults. The sandboxing approach mirrors Codex CLI implementation, maintaining consistency across interfaces.
Personality Modes Adapt to Developer Preferences
Developers choose between terse pragmatic style or conversational empathetic interactions using the /personality command. This preference applies across app, CLI, and IDE extension without capability changes. The execution quality remains identical regardless of communication style selection.
Some developers prefer blunt execution-focused partners while others value communicative engagement. The personality toggle accommodates these working style differences without forcing a single interaction paradigm.
Availability and Pricing Structure
| Plan Type | Access Level | Rate Limits | Additional Credits |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, Enterprise, Edu | Full access across CLI, web, IDE, app | Standard (doubled temporarily) | Purchase option available |
| ChatGPT Free, Go | Limited-time access | Basic | Not applicable |
The macOS app launched February 2, 2026 with Windows version in development. Access requires joining the waitlist at openai.com/form/codex-app. Usage integrates with ChatGPT subscription login credentials. OpenAI doubled rate limits for all paid plans during the limited-time free access period.
Is the Codex app included with existing ChatGPT subscriptions?
Yes. ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, Enterprise, and Edu subscribers receive Codex access across all interfaces including the new app. Usage counts toward subscription limits with optional additional credit purchases. Free and Go users get temporary limited access.
Adoption Metrics and Market Position
Since GPT-5.2-Codex launched mid-December 2025, overall Codex usage doubled. More than one million developers used Codex in the month preceding the app announcement. The desktop application represents OpenAI’s strategic response to Anthropic’s Claude Code, which already offered macOS integration.
TechCrunch noted the app incorporates “many of the agentic practices that have become popular in the past year” less than two months after GPT-5.2-Codex release. OpenAI aims to achieve parity or outpace Claude apps through features like background automations and multi-personality support.
Future Development Roadmap
OpenAI plans Windows version availability, faster inference speeds, and expanded model capabilities. Multi-agent workflow refinements will address real-world feedback about parallel work management and context preservation when switching between agents.
Future Automations will support cloud-based triggers for continuous background operation independent of local machine state. This evolution enables always-on agent supervision without requiring open computers. The development philosophy centers on closing the gap between frontier model capabilities and practical accessibility.
Technical Requirements and Setup
The Codex app requires macOS with ChatGPT login credentials. Join the waitlist at openai.com/form/codex-app to request access. The application integrates existing Codex CLI and IDE extension configurations automatically without manual migration.
Developers access documentation at developers.openai.com/codex/app for complete setup instructions. The open-source Codex CLI repository at github.com/openai/codex provides technical implementation details. Command-line users install via npm with npm i -g @openai/codex or Homebrew with brew install --cask codex.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Codex app work with multiple programming languages simultaneously?
Yes. The Codex app supports polyglot development across all languages the underlying GPT-5.2-Codex model understands. Multiple agents can work on different language components in parallel threads within the same project workspace.
How does Codex handle version control conflicts between multiple agents?
Codex uses worktree implementation where each agent operates on an isolated code copy. You review changes before merging, preventing direct conflicts. Agents don’t write to your local git state until you explicitly approve their work.
What subscription level is required for Codex Automations?
Automations are available to ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, Enterprise, and Edu subscribers. Free and Go users have limited-time basic access without automation features during the promotional period.
Can I create custom Skills for proprietary internal tools?
Yes. The Codex app provides a dedicated interface for creating custom skills. You check them into your repository to share across your team. Skills bundle instructions, resources, and scripts specific to your workflows.
Does the Codex app work offline?
No. Codex requires internet connectivity to access OpenAI’s models. The sandboxed environment restricts network access by default, but the agent itself needs connection to function. Cached web search provides some offline-like capabilities for documentation.
How do I switch from Claude Code to Codex app?
Join the Codex app waitlist at openai.com/form/codex-app, log in with ChatGPT credentials once approved, and the app automatically imports your existing Codex CLI and IDE configurations. No manual project migration is needed.
What happens when an Automation fails?
Failed automation results appear in the review queue with error details. You can examine the agent’s work, adjust instructions or skills, and reschedule the automation. The queue preserves all attempt history for debugging.
Can I use Codex app with GitHub Copilot simultaneously?
Yes. Codex app operates independently from IDE extensions like GitHub Copilot. You can use both tools concurrently, with Copilot handling inline suggestions while Codex manages larger task-based workflows in separate threads.