Software security has always been a race between defenders and attackers and defenders are losing ground. With over 40,000 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) reported in 2024 alone and roughly 1.2% of code commits introducing bugs, security teams face an overwhelming challenge. OpenAI’s answer is Aardvark, a GPT-5 powered autonomous agent that analyzes code repositories, detects vulnerabilities, validates exploits, and proposes fixes all without slowing down development.
Launched on October 30, 2025, Aardvark represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach software security: from reactive patching to continuous, AI-driven protection that works alongside human teams.
Table of Contents
What Is OpenAI Aardvark?
OpenAI Aardvark is an agentic security researcher an AI system that autonomously scans source code to identify security flaws, assess their exploitability, prioritize severity, and recommend targeted patches. Unlike static analysis tools or vulnerability scanners that pattern-match against known issues, Aardvark uses large language model reasoning to understand code behavior the way a human security expert would.
An Autonomous Security Researcher
The key word is “agentic.” Aardvark doesn’t just flag suspicious code patterns, it actively investigates them. It reads documentation, writes test cases, runs exploits in isolated sandboxes, and explains its findings in plain language with step-by-step annotations. Matt Knight, OpenAI’s VP, noted that developers found real value in how Aardvark “clearly explained problems and guided them to fixes”.
How It Differs From Traditional Tools
Traditional security tools rely on techniques like fuzzing (random input testing), software composition analysis (dependency checking), or static code analysis (pattern matching). Aardvark, by contrast, combines GPT-5’s reasoning capabilities with tool use; it can analyze entire repositories with context that older models couldn’t handle, thanks to GPT-5’s expanded context window.
This means Aardvark can catch subtle, context-dependent vulnerabilities that only surface under specific conditions, bugs that traditional scanners routinely miss.
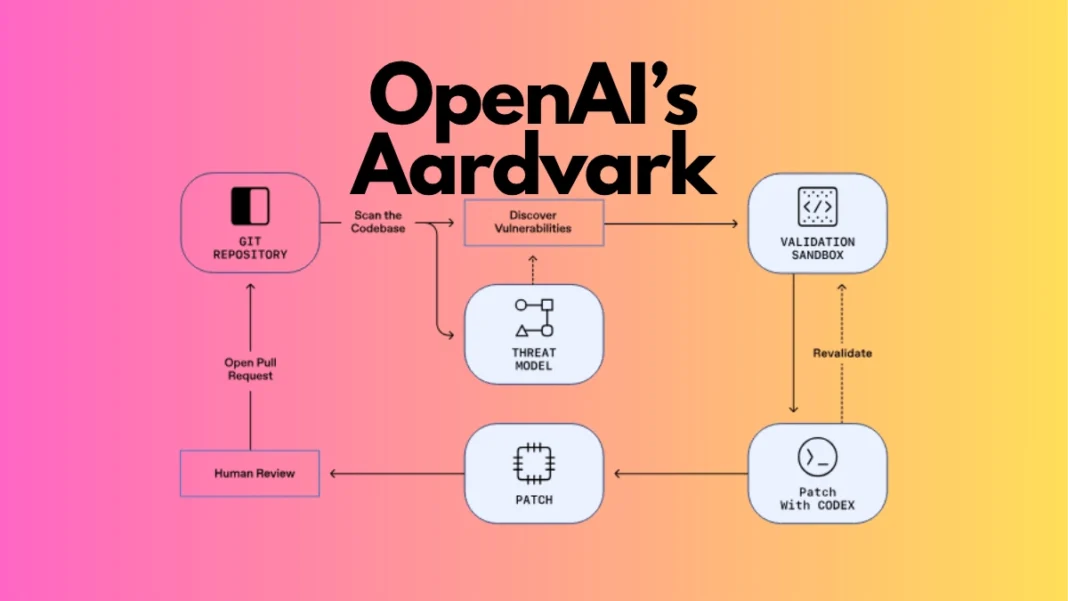
How Aardvark Works: The Four-Stage Pipeline
Aardvark operates through a multi-stage workflow designed to mirror how experienced security researchers approach code review.
Stage 1: Repository Analysis and Threat Modeling
When first connected to a codebase, Aardvark analyzes the full repository to build a threat model and a comprehensive understanding of the project’s architecture, security objectives, and potential attack surfaces. This foundational step allows Aardvark to contextualize every subsequent scan against the system’s actual security requirements.
Stage 2: Commit-Level Vulnerability Scanning
Aardvark monitors every code commit, comparing new changes against both the full repository and its threat model. For newly connected repositories, it scans historical commits to identify pre-existing vulnerabilities. Each potential issue is documented with inline code annotations and explanations that walk developers through the problem.
Stage 3: Sandbox Validation and Exploit Testing
This is where Aardvark distinguishes itself. Instead of simply flagging possible issues, it attempts to trigger each vulnerability in an isolated sandbox environment to confirm it’s genuinely exploitable. This validation step dramatically reduces false positives, a chronic problem with legacy scanners that wastes developer time.
Stage 4: Automated Patch Generation via Codex
Once a vulnerability is confirmed, Aardvark integrates with OpenAI Codex to generate a proposed fix. The patch is then scanned by Aardvark itself before being presented to developers for human review and one-click application. This closed-loop approach keeps security integrated into the development workflow without creating bottlenecks.
Key Features That Set Aardvark Apart
Human-Like Code Reasoning
Aardvark doesn’t just search for known vulnerability signatures. It reasons about code behavior, understanding how different components interact and where complex edge cases might create security gaps. This reasoning ability lets it find bugs that occur only under specific, multi-step conditions the kind attackers actively hunt for.
LLM-Powered Analysis vs Traditional Fuzzing
Traditional tools like fuzzers generate random inputs to stress-test applications, while static analyzers check code against predefined rules. Aardvark uses LLM-powered tool use it can read documentation, write custom test scripts, interpret error messages, and adapt its approach based on what it discovers. This flexibility makes it effective across different programming languages, frameworks, and architectural patterns.
Integration With Existing Workflows
Aardvark connects directly to GitHub, fitting seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines. Security findings appear as annotated reports in familiar formats, and proposed patches can be reviewed and merged through standard pull request workflows. This developer-first design ensures security doesn’t become a productivity bottleneck.
Aardvark’s Real-World Performance
92% Detection Rate on Benchmark Tests
In testing against curated “golden” repositories containing known and synthetically injected vulnerabilities, Aardvark achieved a 92% recall rate meaning it successfully identified 92 out of every 100 real security flaws. This high detection rate, combined with its low false-positive rate due to sandbox validation, makes it far more reliable than conventional automated scanners.
CVE Discoveries in Open Source Projects
Aardvark has already been applied to open-source codebases, where it discovered numerous previously unknown vulnerabilities. OpenAI has responsibly disclosed these findings, with ten receiving official CVE identifiers a testament to their real-world severity. The company plans to offer pro-bono scanning for select non-commercial open-source projects to strengthen the broader software ecosystem.
Early Results From Enterprise Partners
Aardvark has been running continuously across OpenAI’s internal codebases and with external alpha partners for several months. Partners have highlighted the depth of its analysis, particularly its ability to surface issues that traditional tools overlook. At OpenAI itself, Aardvark has “surfaced meaningful vulnerabilities and contributed to OpenAI’s defensive posture”.
Aardvark vs Traditional Security Tools
| Feature | Aardvark (AI-Powered) | Traditional Scanners |
| Analysis Method | LLM reasoning + tool use | Pattern matching, fuzzing, static rules |
| Context Awareness | Full repository understanding | Limited to code snippets or dependencies |
| Exploit Validation | Sandbox testing confirms exploitability | Flags potential issues without validation |
| False Positives | Low (validated vulnerabilities) | High (many flagged issues aren’t exploitable) |
| Patch Suggestions | AI-generated, context-aware fixes | Manual patching required |
| Learning Ability | Adapts reasoning to new codebases | Static rule sets, periodic updates |
| Complex Vulnerabilities | Finds multi-condition edge cases | Misses context-dependent flaws |
Who Should Use Aardvark?
Enterprise Development Teams
Organizations shipping software at scale face constant pressure to balance speed with security. Aardvark provides continuous protection without slowing release cycles, making it ideal for fast-moving product teams. Companies dealing with sensitive data or regulatory compliance requirements will particularly benefit from its validated vulnerability reports.
Open Source Project Maintainers
Maintainers often lack dedicated security resources. Aardvark’s pro-bono offering for non-commercial open-source projects democratizes access to enterprise-grade security research, helping critical infrastructure projects stay secure.
Security-First Organizations
For teams where security is paramount in fintech, healthcare, government contractors Aardvark offers a defense-in-depth layer that complements human security teams. Its ability to find subtle, exploitable bugs makes it valuable for organizations facing sophisticated threat actors.
Limitations and Considerations
Private Beta Constraints
Aardvark is currently available only through a private beta program, with limited slots and a focus on gathering feedback to refine the system. There’s no publicly disclosed pricing, though OpenAI has stated it will “broaden availability as we learn”. Beta participants must use GitHub Cloud integration and actively provide feedback.
False Positive Management
While Aardvark’s sandbox validation significantly reduces false positives, no automated system is perfect. Beta users can report inaccurate flags directly through the dashboard, helping refine the model’s precision before wider release.
Human Review Requirements
Aardvark is designed to augment, not replace, human security experts. All proposed patches require human review before deployment, and complex architectural decisions still need experienced judgment. Think of Aardvark as a force multiplier for your security team, not a substitute.
How to Join the Aardvark Private Beta
Eligibility Requirements
OpenAI is prioritizing organizations and open-source projects that can provide meaningful feedback across diverse environments. Enterprise development teams, major open-source projects, and security-focused organizations are ideal candidates.
Application Process
Interested parties can apply through OpenAI’s official beta signup form. The application asks about your codebase size, tech stack, security maturity, and willingness to collaborate with OpenAI’s team to refine detection workflows.
What to Expect
Beta participants gain early access to Aardvark with direct support from OpenAI engineers. The company has confirmed it will not train models on your code during the beta program, a critical privacy assurance for enterprises. You’ll receive continuous vulnerability reports as your team commits code, with clear explanations and actionable patch suggestions.
The Future of AI-Powered Security Research
Aardvark is part of a broader industry shift toward autonomous DevSecOps. Throughout October 2025, competitors including Anthropic and Microsoft released similar AI security agents, signaling that agentic security research is becoming the new standard. With 40,000+ CVEs reported annually and a growing attacker sophistication gap, tools like Aardvark could fundamentally rebalance the defender-attacker equation.
As GPT-5’s capabilities mature and Aardvark’s training improves through real-world deployment, we can expect even higher accuracy, support for more languages and frameworks, and tighter integration with security orchestration platforms. OpenAI’s updated coordinated disclosure policy positions Aardvark for sustainable, long-term collaboration with developers rather than creating pressure through rigid timelines.
Comparison Table: Aardvark vs Competing AI Security Tools
| Tool | AI Model | Key Strength | Availability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Aardvark | GPT-5 | LLM reasoning + sandbox validation | Private beta | Enterprise teams, open source |
| GitHub Advanced Security | Proprietary | Native GitHub integration | Generally available | GitHub-native workflows |
| XBOW | Custom agents | Offensive security focus | Commercial | Penetration testing teams |
| Mindgard | ML-specific | AI model vulnerabilities | Commercial | AI/ML pipeline security |
| Google Duet AI | Proprietary | GCP integration | Limited availability | Google Cloud users |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is Aardvark different from traditional vulnerability scanners?
Traditional scanners use pattern matching, fuzzing, or static analysis to flag potential issues often generating high false positives. Aardvark uses GPT-5’s reasoning to understand code context, validates vulnerabilities by actually exploiting them in sandboxes, and proposes specific fixes. It finds complex, multi-condition bugs that conventional tools miss.
Does Aardvark replace human security teams?
No. Aardvark is designed to augment human experts, not replace them. It handles continuous monitoring and initial analysis at scale, but all patches require human review before deployment. Think of it as a force multiplier that frees security teams to focus on complex architectural decisions.
How accurate is Aardvark at finding real vulnerabilities?
In benchmark testing on repositories with known vulnerabilities, Aardvark achieved 92% recall, meaning it successfully identified 92 out of every 100 real security flaws. It has also discovered numerous vulnerabilities in open-source projects, with 10 receiving official CVE identifiers.
Will OpenAI train on my code if I use Aardvark?
OpenAI has explicitly stated it will not train models on your code during the private beta program. This is a key privacy assurance for enterprises handling sensitive or proprietary codebases.
How much does Aardvark cost?
Pricing has not been publicly disclosed. Aardvark is currently in private beta with limited availability. OpenAI plans to offer pro-bono scanning for select non-commercial open-source projects and will announce commercial pricing as the platform matures.
Can Aardvark work with languages other than Python?
While specific language support hasn’t been fully detailed, Aardvark’s LLM-powered approach allows it to reason about code across different programming languages and frameworks, unlike rule-based scanners limited to specific languages. Beta feedback will help refine multi-language support.
Featured Snippet Boxes
What is OpenAI Aardvark?
OpenAI Aardvark is a GPT-5 powered autonomous security agent that scans code repositories to identify vulnerabilities, validate their exploitability through sandbox testing, and propose AI-generated fixes. Unlike traditional scanners, it uses LLM reasoning to understand code behavior like a human security researcher, achieving 92% detection accuracy on benchmark tests.
How does Aardvark find vulnerabilities?
Aardvark follows a four-stage pipeline: (1) analyzes the full repository to build a threat model, (2) scans each commit for vulnerabilities against that model, (3) validates findings by triggering exploits in an isolated sandbox, and (4) generates targeted patches using OpenAI Codex. This approach reduces false positives and provides actionable fixes.
Who can access Aardvark?
Aardvark is currently in private beta, available to select enterprise teams and open-source maintainers who apply through OpenAI’s beta signup form. OpenAI plans to offer pro-bono scanning for non-commercial open-source projects and will broaden access based on beta feedback.
Source: OpenAI